Cytokine responses to Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection differ between patient cohorts that have different clinical courses of infection
- PMID: 25398383
- PMCID: PMC4237739
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-014-0580-6
Cytokine responses to Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection differ between patient cohorts that have different clinical courses of infection
Abstract
Background: The clinical course of Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection is unpredictable and bacterial virulence, host immune response and patient characteristics are among the factors that contribute to the clinical course of infection. To investigate the relationship between cytokine response and clinical outcome, circulating cytokine levels were investigated in response to S. aureus bloodstream infection in patients with different clinical courses of infection.
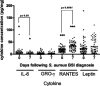
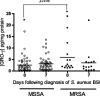
Methods: A prospective study was carried out in 61 patients with S. aureus bloodstream infection and circulating levels of IL-6, GRO-γ, RANTES and leptin were assessed over the course of the infection. Levels were compared in patients with complicated courses of infection (e.g. infective endocarditis) versus uncomplicated courses of S. aureus bloodstream infection and methicillin-resistant S. aureus Vs methicillin-susceptible S. aureus infection.
Results: Significantly lower leptin levels (p < 0.05) and significantly higher IL-6 levels (p < 0.05) were detected at laboratory diagnosis in patients with complicated compared to uncomplicated S. aureus bloodstream infection. Significantly higher levels of GRO-γ were associated with MRSA infection compared to MSSA infection.
Conclusions: IL-6 may be an early inflammatory marker of complicated S. aureus bloodstream infection. Leptin may be protective against the development of a complicated S. aureus bloodstream infection.
Figures


References
-
- Fowler VG, Jr, Nelson CL, McIntyre LM, Kreiswirth BN, Monk A, Archer GL, Federspiel J, Naidich S, Remortel B, Rude T, Brown P, Reller LB, Corey GR, Gill SR. Potential associations between hematogenous complications and bacterial genotype in Staphylococcus aureusinfection. J Infect Dis. 2007;196(5):738–747. doi: 10.1086/520088. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takata T, Miyazaki M, Futo M, Hara S, Shiotsuka S, Kamimura H, Yoshimura H, Matsunaga A, Nishida T, Ishikura H, Tamura K, Tsuji BT. Presence of both heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate resistance and beta-lactam antibiotic-induced vancomycin resistance phenotypes is associated with the outcome in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusbloodstream infection. Scand J Infect Dis. 2013;45(3):203–212. doi: 10.3109/00365548.2012.723221. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Verkaik NJ, Dauwalder O, Antri K, Boubekri I, de Vogel CP, Badiou C, Bes M, Vandenesch F, Tazir M, Hooijkaas H, Verbrugh HA, van Belkum A, Etienne J, Lina G, Ramdani-Bouguessa N, van Wamel WJ. Immunogenicity of toxins during Staphylococcus aureusinfection. Clin Infect Dis. 2010;50(1):61–68. doi: 10.1086/648673. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

