Pulmonary co-infection with Nocardia and Aspergillus in a patient with adult-onset Still's disease receiving steroids and tacrolimus
- PMID: 25398925
- PMCID: PMC4244375
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-207335
Pulmonary co-infection with Nocardia and Aspergillus in a patient with adult-onset Still's disease receiving steroids and tacrolimus
Abstract
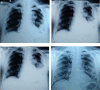
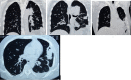
Patients on immunosuppression are at risk of unusual infections. We present a man diagnosed to have adult-onset Still's disease who, on high-dose oral steroid and tacrolimus, developed a cavitating pneumonia due to co-infection with Aspergillus flavus and Nocardia. Timely diagnosis and institution of appropriate therapy resulted in a favourable clinical outcome. Such co-infection in a patient receiving tacrolimus is rare in the published literature. This case serves to emphasise the need to be vigilant for unusual infections in patients who are immunosuppressed, either due to drugs or underlying disease condition.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
