Does combined peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-agonist and pravastatin therapy attenuate the onset of diabetes-induced experimental nephropathy?
- PMID: 25399210
- PMCID: PMC4362144
Does combined peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-agonist and pravastatin therapy attenuate the onset of diabetes-induced experimental nephropathy?
Abstract
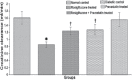
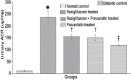
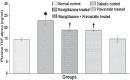
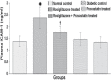
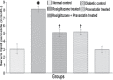
Objectives: To investigate the combined effects of rosiglitazone and pravastatin on renal functions in early streptozotocin induced diabetic nephropathy (DN).
Methods: This study was carried out at King Khalid University Hospital Animal House, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia from August 2013 to February 2014. Fifty male Wistar rats were assigned to normal control rats and diabetic rats that received saline, rosiglitazone, pravastatin, or rosiglitazone+pravastatin for 2 months. Their weight range was 230-250 gm, and age range was from 18-20 weeks. At the end of experiment, creatinine clearance, and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (ACR) were measured. Blood samples were analyzed for transferrin, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), lipid profile, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), and lipid peroxide.
Results: Rosiglitazone treatment increased creatinine clearance and plasma transferrin, and decreased urinary ACR, HbA1c, plasma TNF-α, ICAM-1, and serum lipid peroxide levels without affecting the altered lipid profile. Pravastatin treatment produced similar results and normalized the lipid alteration. The combination of rosiglitazone and pravastatin was more effective in attenuating the diabetes-induced nephropathy compared with treatment with either drug alone.
Conclusion: The combination strategy of rosiglitazone and pravastatin may provide a potential synergistic renoprotective effect against DN by improving renal functions and reducing indices of DN.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renoprotective effect of rosiglitazone through the suppression of renal intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Endocrinol Invest. 2008 Dec;31(12):1069-74. doi: 10.1007/BF03345654. J Endocrinol Invest. 2008. PMID: 19246972
-
Effects of pravastatin or 12/15 lipoxygenase pathway inhibitors on indices of diabetic nephropathy in an experimental model of diabetic renal disease.Saudi Med J. 2012 Jun;33(6):608-16. Saudi Med J. 2012. PMID: 22729114
-
The low dose combination of fenofibrate and rosiglitazone halts the progression of diabetes-induced experimental nephropathy.Eur J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun 25;636(1-3):137-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.03.002. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Eur J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20347778
-
Estimating the predictive validity of diabetic animal models in rosiglitazone studies.Obes Rev. 2015 Jun;16(6):498-507. doi: 10.1111/obr.12278. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Obes Rev. 2015. PMID: 25786332 Review.
-
Diabetes as a negative risk factor for abdominal aortic aneurysm - does the disease aetiology or the treatment provide the mechanism of protection?Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013 May;11(3):293-8. doi: 10.2174/1570161111311030003. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22724482 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Pravastatin in Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy in Rats.Iran J Pharm Res. 2018 Fall;17(4):1413-1419. Iran J Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 30568699 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing diabetic kidney disease animal models: Insights from a meta-analytic approach.Animal Model Exp Med. 2023 Oct;6(5):433-451. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12350. Epub 2023 Sep 18. Animal Model Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37723622 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Balakumar P, Arora MK, Singh M. Emerging role of PPAR ligands in the management of diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol Res. 2009;60:170–173. - PubMed
-
- Soldatos G, Cooper ME. Diabetic nephropathy: important pathophysiologic mechanisms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2008;82(Suppl 1):S75–S79. - PubMed
-
- Kanwar YS, Wada J, Sun L, Xie P, Wallner EI, Chen S, et al. Diabetic nephropathy: mechanisms of renal disease progression. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2008;233:4–11. - PubMed
-
- Rutledge JC, Ng KF, Aung HH, Wilson DW. Role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Neels JG, Grimaldi PA. Physiological functions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor b. Physiol Rev. 2014;94:795–858. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
