Blockade of mGluR5 in the nucleus accumbens shell but not core attenuates heroin seeking behavior in rats
- PMID: 25399651
- PMCID: PMC4261128
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2014.93
Blockade of mGluR5 in the nucleus accumbens shell but not core attenuates heroin seeking behavior in rats
Abstract
Aim: Glutamatergic neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens (NAc) is crucial for the relapse to heroin seeking. The aim of this study was to determine whether mGluR5 in the NAc core or shell involved in heroin seeking behavior in rats.
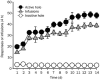
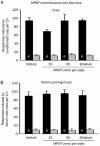
Methods: Male SD rats were self-administered heroin under a fixed-ratio 1 (FR1) reinforcement schedule for 14 d, and subsequently withdrawn for 2 weeks. The selective mGluR5 antagonist 2-methyl-6-phenylethynyl-pyridine (MPEP, 5, 15 and 50 nmol per side) was then microinjected into the NAc core or shell 10 min before a heroin-seeking test induced by context, cues or heroin priming.
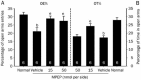
Results: Microinjection of MPEP into the NAc shell dose-dependently decreased the heroin seeking induced by context, cues or heroin priming. In contrast, microinjection of MPEP into the NAc core did not alter the heroin seeking induced by cues or heroin priming. In addition, microinjection with MPEP (15 nmol per side) in the NAc shell reversed both the percentage of open arms entries (OE%) and the percentage of time spent in open arms (OT%) after heroin withdrawal. Microinjection of MPEP (50 nmol per side) in the striatum as a control location did not affect the heroin seeking behavior. Microinjection of MPEP in the 3 locations did not change the locomotion activities.
Conclusion: Blockade of mGluR5 in NAc shell in rats specifically suppresses the relapse to heroin-seeking and anxiety-like behavior, suggesting that mGluR5 antagonists may be a potential candidate for the therapy of heroin addiction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Activation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens shell attenuates context-induced relapse to heroin seeking.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 Oct;31(10):2197-209. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300977. Epub 2005 Dec 7. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006. PMID: 16341024 Free PMC article.
-
Galantamine attenuates the heroin seeking behaviors induced by cues after prolonged withdrawal in rats.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Jun;62(8):2515-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2012.01.031. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22342742
-
Group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated activation of PKC gamma in the nucleus accumbens core promotes the reinstatement of cocaine seeking.Addict Biol. 2015 Mar;20(2):285-96. doi: 10.1111/adb.12122. Epub 2014 Feb 9. Addict Biol. 2015. PMID: 24506432 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes as cellular mediators of cue reactivity in addiction.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2021 Feb;56:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2020.07.009. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32862045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurobiology of abstinence-induced reward-seeking in males and females.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021 Jan;200:173088. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.173088. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2021. PMID: 33333134 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of GABRD Gene Methylation in the Nucleus Accumbens in Heroin-Seeking Behavior in Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 21;11:612200. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.612200. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33551813 Free PMC article.
-
Female rats self-administer heroin by vapor inhalation.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020 Dec;199:173061. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2020.173061. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2020. PMID: 33164848 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Impairment and Persistent Upregulation of mGlu5 Receptor following Morphine Abstinence: Implications of an mGlu5-MOPr Interaction.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016 Jul 5;19(7):pyw011. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw011. Print 2016 Jul. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26861145 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular windows into the human brain for psychiatric disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 May;24(5):653-673. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0125-2. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29955163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-acetylaspartylglutamate Inhibits Heroin Self-Administration and Heroin-Seeking Behaviors Induced by Cue or Priming in Rats.Neurosci Bull. 2017 Aug;33(4):396-404. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0140-3. Epub 2017 May 22. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28534263 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

