Trends in blood pressure among adults with hypertension: United States, 2003 to 2012
- PMID: 25399687
- PMCID: PMC11262548
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04012
Trends in blood pressure among adults with hypertension: United States, 2003 to 2012
Abstract
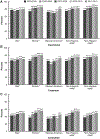
The aim of this study is to describe trends in the awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension; mean blood pressure; and the classification of blood pressure among US adults 2003 to 2012. Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003 to 2012, a total of 9255 adult participants aged ≥18 years were identified as having hypertension, defined as measured blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or taking prescription medication for hypertension. Awareness and treatment among hypertensive adults were ascertained via an interviewer administered questionnaire. Controlled hypertension among hypertensive adults was defined as systolic blood pressure <140 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure <90 mm Hg. Blood pressure was categorized as optimal blood pressure, prehypertension, and stage I and stage II hypertension. Between 2003 and 2012, the percentage of adults with controlled hypertension increased (P-trend <0.01). Hypertensive adults with optimal blood pressure and with prehypertension increased from 13% to 19% and 27% to 33%, respectively (P-trend <0.01 for both groups). Among hypertensive adults who were taking antihypertensive medication, uncontrolled hypertension decreased from 38% to 30% (P-trend <0.01). Similarly, a decrease in mean systolic blood pressure was observed (P-trend <0.01); however, mean diastolic blood pressure remained unchanged. The trend in the control of blood pressure has improved among hypertensive adults resulting in a higher percentage with blood pressure at the optimal or prehypertension level and a lower percentage in stage I and stage II hypertension. Overall, mean systolic blood pressure decreased as did the prevalence of uncontrolled hypertension among the treated hypertensive population.
Keywords: blood pressure; epidemiology; hypertension; prevention and control; therapeutics.
© 2014 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Control of hypertension: is the goal reached?Hypertension. 2015 Jan;65(1):25-6. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.04256. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 25399686 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–2572. - PubMed
-
- Farley TA, Dalal MA, Mostashari F, Frieden TR. Deaths preventable in the U.S. by improvements in use of clinical preventive services. Am J Prev Med. 2010;38:600–609. - PubMed
-
- Gu Q, Dillon CF, Burt VL, Gillum RF. Association of hypertension treatment and control with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality among US adults with hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2010;23:38–45. - PubMed
-
- Collins R, Peto R, MacMahon S, Hebert P, Fiebach NH, Eberlein KA, Godwin J, Qizilbash N, Taylor JO, Hennekens CH. Lancet. 1990; 335: 827–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

