A MyD88-JAK1-STAT1 complex directly induces SOCS-1 expression in macrophages infected with Group A Streptococcus
- PMID: 25399770
- PMCID: PMC4654310
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2014.107
A MyD88-JAK1-STAT1 complex directly induces SOCS-1 expression in macrophages infected with Group A Streptococcus
Abstract
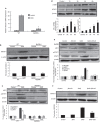
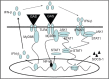
Some pathogens can use host suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS-1), an important negative-feedback molecule, as the main mode of immune evasion. Here we found that group A Streptococcus (GAS) is capable of inducing SOCS-1 expression in RAW264.7 and BMDM macrophages. IFN-β plays a role in GAS-induced SOCS-1 expression in macrophages following the induction of cytokine expression by GAS, representing the classical pathway of SOCS-1 expression. However, GAS also induced STAT1 activation and SOCS-1 expression when GAS-infected cells were incubated with anti-IFN-β monoclonal antibody in this study. Moreover, upon comparing TLR4(-/-) BMDM macrophages with wild-type (WT) cells, we found that TLR4 also plays an essential role in the induction of SOCS-1. MyD88, which is an adaptor protein for TLR4, contributes to STAT1 activation and phosphorylation by forming a complex with Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) in macrophages. GAS-stimulated expression of STAT1 was severely impaired in MyD88(-/-) macrophages, whereas expression of JAK1 was unaffected, suggesting that MyD88 was involved in STAT1 expression and phosphorylation. Together, these data demonstrated that in addition to IFN-β signaling and MyD88 complex formation, JAK1 and STAT1 act in a novel pathway to directly induce SOCS-1 expression in GAS-infected macrophages, which may be more conducive to rapid bacterial infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astrocyte TLR4 activation induces a proinflammatory environment through the interplay between MyD88-dependent NFκB signaling, MAPK, and Jak1/Stat1 pathways.Glia. 2011 Feb;59(2):242-55. doi: 10.1002/glia.21094. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21125645
-
Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins indirectly regulate toll-like receptor signaling in innate immune cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 24;279(52):54708-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410992200. Epub 2004 Oct 18. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15491991
-
SOCS1 regulates the IFN but not NFkappaB pathway in TLR-stimulated human monocytes and macrophages.J Immunol. 2008 Dec 1;181(11):8018-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.11.8018. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 19017994 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS Proteins Participate in the Regulation of Innate Immune Response Caused by Viruses.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 25;11:558341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.558341. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Responses of innate immune cells to group A Streptococcus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Oct 2;4:140. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00140. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25325020 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of experimental acute lung injury by exosomal miR-7704 from mesenchymal stromal cells acts through M2 macrophage polarization.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Dec 14;35(1):102102. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102102. eCollection 2024 Mar 12. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 38222299 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of STAT1 and IRF1 enhancers and the influence of SNPs.BMC Mol Biol. 2017 Mar 9;18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12867-017-0084-1. BMC Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28274199 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular HSP90α Induces MyD88-IRAK Complex-Associated IKKα/β-NF-κB/IRF3 and JAK2/TYK2-STAT-3 Signaling in Macrophages for Tumor-Promoting M2-Polarization.Cells. 2022 Jan 11;11(2):229. doi: 10.3390/cells11020229. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053345 Free PMC article.
-
From Beef to Bees: High-Throughput Kinome Analysis to Understand Host Responses of Livestock Species to Infectious Diseases and Industry-Associated Stress.Front Immunol. 2020 May 15;11:765. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00765. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32499776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Defective monocyte oxidative burst predicts infection in alcoholic hepatitis and is associated with reduced expression of NADPH oxidase.Gut. 2017 Mar;66(3):519-529. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310378. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Gut. 2017. PMID: 26860769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 1Miettinen M, Lehtonen A, Julkunen I, Matikainen S. Lactobacilli and Streptococci activate NF-kappa B and STAT signaling pathways in human macrophages. J Immunol 2000; 164: 3733–3740. - PubMed
-
- 4Bisno AL, Brito MO, Collins CM. Molecular basis of group A streptococcal virulence. Lancet Infect Dis 2003; 3: 191–200. - PubMed
-
- 5Chhatwal GS, McMillan DJ. Uncovering the mysteries of invasive streptococcal diseases. Trends Mol Med 2005; 11: 152–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

