Outcomes and resource utilization in ST-elevation myocardial infarction in the United States: evidence for socioeconomic disparities
- PMID: 25399775
- PMCID: PMC4338692
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001057
Outcomes and resource utilization in ST-elevation myocardial infarction in the United States: evidence for socioeconomic disparities
Abstract
Background: Socioeconomic status (SES) as reflected by residential zip code status may detrimentally influence a number of prehospital clinical, access-related, and transport variables that influence outcome for patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) undergoing reperfusion. We sought to analyze the impact of SES on in-hospital mortality, timely reperfusion, and cost of hospitalization following STEMI.
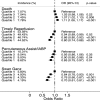
Methods and results: We used the 2003-2011 Nationwide Inpatient Sample database for this analysis. All hospital admissions with a principal diagnosis of STEMI were identified using ICD-9 codes. SES was assessed using median household income of the residential zip code for each patient. There was a significantly higher mortality among the lowest SES quartile as compared to the highest quartile (OR [95% CI]: 1.11 [1.06 to 1.17]). Similarly, there was a highly significant trend indicating a progressively reduced timely reperfusion among patients from lower quartiles (OR [95% CI]: 0.80 [0.74 to 0.88]). In addition, there was a lower utilization of circulatory support devices among patients from lower as compared to higher zip code quartiles (OR [95% CI]: 0.85 [0.75 to 0.97]). Furthermore, the mean adjusted cost of hospitalization among quartiles 2, 3, and 4, as compared to quartile 1 was significantly higher by $913, $2140, and $4070, respectively.
Conclusions: Patients residing in zip codes with lower SES had increased in-hospital mortality and decreased timely reperfusion following STEMI as compared to patients residing in higher SES zip codes. The cost of hospitalization of patients from higher SES quartiles was significantly higher than those from lower quartiles.
Keywords: STEMI; acute myocardial infarction; mortality; socioeconomic status; zip code.
© 2014 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


References
-
- Bonow RO, Grant AO, Jacobs AK. The cardiovascular state of the union: confronting healthcare disparities. Circulation. 2005; 111:1205-1207. - PubMed
-
- Mensah GA, Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Greenlund KJ, Croft JB. State of disparities in cardiovascular health in the United States. Circulation. 2005; 111:1233-1241. - PubMed
-
- Winkleby MA, Kraemer HC, Ahn DK, Varady AN. Ethnic and socioeconomic differences in cardiovascular disease risk factors: findings for women from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. JAMA. 1998; 280:356-362. - PubMed
-
- Smedley BD, Stith AY, Nelson AR. Unequal Treatment: Confronting Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Health Care. 2002Washington, DC: National Academy Press - PubMed
-
- Geronimus AT, Bound J, Niedert L. On the Validity of Using Census Geocode Characteristics to Proxy Economic Status. 1993Ann Arbor, MI: Population Studies Center, University of Michigan
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

