Alpha-2-macroglobulin as a radioprotective agent: a review
- PMID: 25400428
- PMCID: PMC4220256
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2014.09.04
Alpha-2-macroglobulin as a radioprotective agent: a review
Abstract
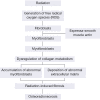
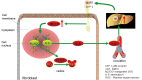
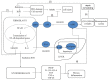
Radiation is an important modality in cancer treatment, and eighty percent of cancer patients need radiotherapy at some point during their clinical management. However, radiation-induced damage to normal tissues restricts the therapeutic doses of radiation that can be delivered to tumours and thereby limits the effectiveness of the treatment. The use of radioprotectors represents an obvious strategy to obtain better tumour control using a higher dose in radiotherapy. However, most of the synthetic radioprotective compounds studied have shown inadequate clinical efficacy owing to their inherent toxicity and high cost. Hence, the development of radioprotective agents with lower toxicity and an extended window of protection has attracted a great deal of attention, and the identification of alternative agents that are less toxic and highly effective is an absolute necessity. Recent studies have shown that alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M) possesses radioprotective effects. α2M is a tetrameric, disulfide-rich plasma glycoprotein that functions as a non-selective inhibitor of different types of non-specific proteases and as a carrier of cytokines, growth factors, and hormones. α2M induces protein factors whose interplay underlies radioprotection, which supports the idea that α2M is the central effector of natural radioprotection in the rat. Pretreatment with α2M has also induced a significant reduction of irradiation-induced DNA damage and the complete restoration of liver and body weight. Mihailović et al. concluded that the radioprotection provided by α2M was in part mediated through cytoprotection of new blood cells produced in the bone marrow; these authors also indicated that an important aspect of the radioprotective effect of amifostine was the result of the induction of the endogenous cytoprotective capability of α2M. The radioprotective effects of α2M are possibly due to antioxidant, anti-fibrosis, and anti-inflammatory functions, as well as the maintenance of homeostasis, and enhancement of the DNA repair and cell recovery processes. This review is the first to summarise the observations and elucidate the possible mechanisms responsible for the beneficial effects of α2M. The lacunae in the existing knowledge and directions for future research are also addressed.
Keywords: Alpha-2-macroglobulin (α2M); ionising radiation; mechanism; radiation-induced fibrosis; radioprotection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of α2‑macroglobulin in the early stage of jaw osteoradionecrosis.Int J Oncol. 2020 Jul;57(1):213-222. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5051. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32377713 Free PMC article.
-
The acute-phase protein alpha2-macroglobulin plays an important role in radioprotection in the rat.Shock. 2009 Jun;31(6):607-14. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31818bb625. Shock. 2009. PMID: 18838941
-
Radioprotective potential of mint: a brief review.J Cancer Res Ther. 2010 Jul-Sep;6(3):255-62. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.73336. J Cancer Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 21119249 Review.
-
Indian Indigenous Fruits as Radioprotective Agents: Past, Present and Future.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(1):53-63. doi: 10.2174/1871520621666210706124315. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34229590 Review.
-
Administration of rat acute-phase protein α(2)-macroglobulin before total-body irradiation initiates cytoprotective mechanisms in the liver.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011 Mar;50(1):167-79. doi: 10.1007/s00411-010-0331-z. Epub 2010 Sep 17. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011. PMID: 20848291
Cited by
-
Preliminary proteomic analysis of human tears in lacrimal adenoid cystic carcinoma and pleomorphic adenoma.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jun 18;16(6):841-848. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.06.02. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37332550 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of α‑2‑macroglobulin on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in radiation injury.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Nov;18(5):4219-4228. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9449. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30221711 Free PMC article.
-
Clear differences in cerebrospinal fluid proteome between women with chronic widespread pain and healthy women - a multivariate explorative cross-sectional study.J Pain Res. 2017 Mar 13;10:575-590. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S125667. eCollection 2017. J Pain Res. 2017. PMID: 28331360 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-2-macroglobulin is involved in the occurrence of early-onset pre-eclampsia via its negative impact on uterine spiral artery remodeling and placental angiogenesis.BMC Med. 2023 Mar 9;21(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02807-9. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 36894970 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of α2‑macroglobulin in the early stage of jaw osteoradionecrosis.Int J Oncol. 2020 Jul;57(1):213-222. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2020.5051. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32377713 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nair CK, Parida DK, Nomura T. Radioprotectors in radiotherapy. J Radiat Res 2001;42:21-37. - PubMed
-
- Ringborg U, Bergqvist D, Brorsson B, et al. The Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care (SBU) systematic overview of radiotherapy for cancer including a prospective survey of radiotherapy practice in Sweden 2001—summary and conclusions. Acta Oncol 2003;42:357-65. - PubMed
-
- Brown DQ, Pittock JW, 3rd, Rubinstein JS. Early results of the screening program for radioprotectors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1982;8:565-70. - PubMed
-
- Cassatt DR, Fazenbaker CA, Bachy CM, et al. Preclinical modeling of improved amifostine (ethyol) use in radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol 2002;12:97-102. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
