Prevention and control of schistosomiasis: a current perspective
- PMID: 25400499
- PMCID: PMC4231879
- DOI: 10.2147/RRTM.S44274
Prevention and control of schistosomiasis: a current perspective
Abstract
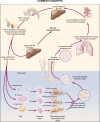
Schistosomiasis is a neglected tropical disease that ranks second only to malaria in terms of human suffering in the tropics and subtropics. Five species are known to infect man and there are currently over 240 million people infected worldwide. The cornerstone of control to date has been mass drug administration with 40 mg/kg of praziquantel but there are problems with this approach. Human and bovine vaccines are in various stages of development. Integrated control, targeting the life cycle, is the only approach that will lead to sustainability and future elimination.
Keywords: mass drug administration; morbidity; schistosomiais; treatment and control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work. Ethical clearance was not required for this review.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis Progress Report (2001−2011) and Strategic Plan (2012−2020). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization Press; 2013. Available from: http://www.who.int/schistosomiasis/resources/en/. Accessed December 9, 2013.
-
- Barry MA, Simon GG, Mistry N, Hotez PJ. Global trends in neglected tropical disease control and elimination: impact on child health. Arch Dis Child. 2013;98(8):635–641. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. The global burden of disease: 2004 update. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization Press; 2008. Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/2004_report_update/en/. Accessed July 16, 2014.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

