The use of natural and synthetic phospholipids as pharmaceutical excipients
- PMID: 25400504
- PMCID: PMC4207189
- DOI: 10.1002/ejlt.201400219
The use of natural and synthetic phospholipids as pharmaceutical excipients
Abstract
In pharmaceutical formulations, phospholipids obtained from plant or animal sources and synthetic phospholipids are used. Natural phospholipids are purified from, e.g., soybeans or egg yolk using non-toxic solvent extraction and chromatographic procedures with low consumption of energy and minimum possible waste. Because of the use of validated purification procedures and sourcing of raw materials with consistent quality, the resulting products differing in phosphatidylcholine content possess an excellent batch to batch reproducibility with respect to phospholipid and fatty acid composition. The natural phospholipids are described in pharmacopeias and relevant regulatory guidance documentation of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA). Synthetic phospholipids with specific polar head group, fatty acid composition can be manufactured using various synthesis routes. Synthetic phospholipids with the natural stereochemical configuration are preferably synthesized from glycerophosphocholine (GPC), which is obtained from natural phospholipids, using acylation and enzyme catalyzed reactions. Synthetic phospholipids play compared to natural phospholipid (including hydrogenated phospholipids), as derived from the number of drug products containing synthetic phospholipids, a minor role. Only in a few pharmaceutical products synthetic phospholipids are used. Natural phospholipids are used in oral, dermal, and parenteral products including liposomes. Natural phospholipids instead of synthetic phospholipids should be selected as phospholipid excipients for formulation development, whenever possible, because natural phospholipids are derived from renewable sources and produced with more ecologically friendly processes and are available in larger scale at relatively low costs compared to synthetic phospholipids. Practical applications: For selection of phospholipid excipients for pharmaceutical formulations, natural phospholipids are preferred compared to synthetic phospholipids because they are available at large scale with reproducible quality at lower costs of goods. They are well accepted by regulatory authorities and are produced using less chemicals and solvents at higher yields. In order to avoid scale up problems during pharmaceutical development and production, natural phospholipid excipients instead of synthetic phospholipids should be selected whenever possible.
Keywords: Emulsifier; Lecithin; Liposomes; Natural phospholipids; Phosphatidylcholine; Solubilizer; Synthetic phospholipids.
Figures


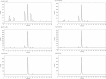
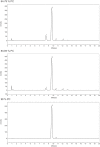
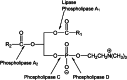
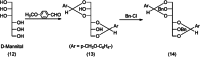


Similar articles
-
Review - An update on the use of oral phospholipid excipients.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017 Oct 15;108:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 12. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28711714 Review.
-
Rationale utilization of phospholipid excipients: a distinctive tool for progressing state of the art in research of emerging drug carriers.J Liposome Res. 2023 Mar;33(1):1-33. doi: 10.1080/08982104.2022.2069809. Epub 2022 May 11. J Liposome Res. 2023. PMID: 35543241 Review.
-
Comparison of the in vitro cytotoxicity among phospholipid-based parenteral drug delivery systems: Emulsions, liposomes and aqueous lecithin dispersions (WLDs).Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019 Jan 15;127:92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.10.018. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 30342174
-
The role of phospholipids in drug delivery formulations - Recent advances presented at the Researcher's Day 2023 Conference of the Phospholipid Research Center Heidelberg.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024 Apr;197:114215. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2024.114215. Epub 2024 Feb 11. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2024. PMID: 38350530
-
Hydrogenated plant-based lecithins as excipients for cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications: A physical-chemical study.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2025 Aug 1;211:107144. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2025.107144. Epub 2025 May 26. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40425131
Cited by
-
Plant-Based Nanovesicular Gel Formulations Applied to Skin for Ameliorating the Anti-Inflammatory Efficiency.Gels. 2024 Aug 10;10(8):525. doi: 10.3390/gels10080525. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39195054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nutraceutical Vegetable Oil Nanoformulations for Prevention and Management of Diseases.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020 Jun 24;10(6):1232. doi: 10.3390/nano10061232. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32599957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid-based surface engineering of PLGA nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery applications.Biomater Res. 2016 Oct 31;20:34. doi: 10.1186/s40824-016-0081-3. eCollection 2016. Biomater Res. 2016. PMID: 27807476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double Peptide-Functionalized Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Coated Liposomes Loaded with Dexamethasone as a Potential Strategy for Active Targeting Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):922. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030922. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940692 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Ingredient-Based Polymeric Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment.Molecules. 2020 Aug 9;25(16):3620. doi: 10.3390/molecules25163620. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32784890 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shurtleff W, Aoyagi A. 2007. History of Soy Lecithin http://www.soyinfocenter.com/HSS/lecithin1.php.
-
- Pepeu G, Vannucchi MG, Di Patre PL. In: Phospholipids: Biochemical, Pharmaceutical, and Analytical Considerations [Proceedings of the 5th International Colloquium on Lecithin; Phospholipids: Biochemical, Pharmaceutical, and Analytical Considerations, Held April 10–12, 1989, in Cannes, France] Hanin I, Pepeu G, editors. New York [u. a.]: Plenum Press; 1990. pp. 43–50.
-
- Vertzoni M, Markopoulos C, Symillides M, Goumas C, et al. Luminal lipid phases after administration of a triglyceride solution of danazol in the fed state and their contribution to the flux of danazol across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Mol. Pharm. 2012;9:1189–1198. - PubMed
-
- Hanin I, Pepeu G. Phospholipids Biochemical, Pharmaceutical, and Analytical Considerations: [Proceedings of the Fifth International Colloquium on Lecithin; Phospholipids: Biochemical, Pharmaceutical, and Analytical Considerations, held April 10–12, 1989, in Cannes, France] New York [u.a.]: Plenum Press; 1990.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
