The interplay of plasticity and adaptation in neural circuits: a generative model
- PMID: 25400577
- PMCID: PMC4214225
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2014.00026
The interplay of plasticity and adaptation in neural circuits: a generative model
Abstract
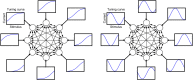
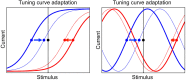
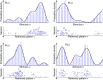
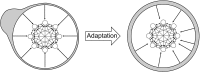
Multiple neural and synaptic phenomena take place in the brain. They operate over a broad range of timescales, and the consequences of their interplay are still unclear. In this work, I study a computational model of a recurrent neural network in which two dynamic processes take place: sensory adaptation and synaptic plasticity. Both phenomena are ubiquitous in the brain, but their dynamic interplay has not been investigated. I show that when both processes are included, the neural circuit is able to perform a specific computation: it becomes a generative model for certain distributions of input stimuli. The neural circuit is able to generate spontaneous patterns of activity that reproduce exactly the probability distribution of experienced stimuli. In particular, the landscape of the phase space includes a large number of stable states (attractors) that sample precisely this prior distribution. This work demonstrates that the interplay between distinct dynamical processes gives rise to useful computation, and proposes a framework in which neural circuit models for Bayesian inference may be developed in the future.
Keywords: Bayesian inference; attractor model; dynamical systems; generative model; sensory adaptation; synaptic plasticity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Network capacity analysis for latent attractor computation.Network. 2003 May;14(2):273-302. Network. 2003. PMID: 12790185
-
From statistical inference to a differential learning rule for stochastic neural networks.Interface Focus. 2018 Dec 6;8(6):20180033. doi: 10.1098/rsfs.2018.0033. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Interface Focus. 2018. PMID: 30443331 Free PMC article.
-
Learning structure of sensory inputs with synaptic plasticity leads to interference.Front Comput Neurosci. 2015 Aug 5;9:103. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2015.00103. eCollection 2015. Front Comput Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26300769 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics on the manifold: Identifying computational dynamical activity from neural population recordings.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021 Oct;70:163-170. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2021.10.014. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34837752 Review.
-
A stable brain from unstable components: Emerging concepts and implications for neural computation.Neuroscience. 2017 Aug 15;357:172-184. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Neuroscience. 2017. PMID: 28602920 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling Neural Adaptation in Auditory Cortex.Front Neural Circuits. 2018 Sep 5;12:72. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2018.00072. eCollection 2018. Front Neural Circuits. 2018. PMID: 30233332 Free PMC article.
-
Itinerancy between attractor states in neural systems.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;40:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2016.05.005. Epub 2016 Jun 16. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 27318972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Time-delay model of perceptual decision making in cortical networks.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 15;14(2):e0211885. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211885. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30768608 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Neuronal Intrinsic Physiology Changes During Development of a Learned Behavior.eNeuro. 2017 Oct 20;4(5):ENEURO.0297-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0297-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Sep-Oct. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 29062887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amit D. J. (1992). Modeling Brain Function: The World of Attractor Neural Networks. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

