Helicobacter pylori regulates TLR4 and TLR9 during gastric carcinogenesis
- PMID: 25400780
- PMCID: PMC4230143
Helicobacter pylori regulates TLR4 and TLR9 during gastric carcinogenesis
Abstract
Objective: To investigated the influence of H. pylori on TLR4 and TLR9 in gastric mucosa during gastric carcinogenesis.
Methods: Gastric biopsy specimens were taken from 148 patients and divided into five groups, including normal group (n = 10), chronic superficial gastritis group (n = 35), atrophy/intestinal metaplasia group (n = 35), dysplasia group (n = 34) and gastric carcinoma group (n = 34). Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of TLR4 and TLR9. Geimsa staining and rapid urea test were used for determine H. pylori infection.
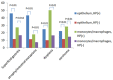
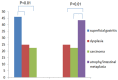
Results: TLR4 was detected in gastric epithelium and monocytes/macrophages in superficial gastritis, atrophy/intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia or carcinoma. TLR9 was mainly accentuated in monocytes/macrophages. TLR4 positive cells in epithelium and in monocytes/macrophages with H. pylori infection were much more than those without H. pylori infection. Similar results were also found in TLR9. When gastric epithelium was accompanied with H. pylori infection, TLR4 was significant higher in superficial gastritis and atrophy/intestinal metaplasia groups compared with dysplasia and carcinoma groups. When gastric epithelium was infected by H. pylori, TLR9 was significant higher in carcinoma group compared with superficial gastritis, atrophy/intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia. TLR4 and TLR9 show significant correlation with the severity of inflammation.
Conclusions: H. pylori infection was associated with increased expression of TLR4 and TLR9 in gastric mucosa. In superficial gastritis and atrophy/intestinal metaplasia the inflammation was predominately mediated by TLR4, while in gastric cancer the inflammation was mainly mediated by TLR9.
Keywords: Expression of Toll-like receptor; H. pylori; gastric carcinogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on gastric carcinoma cells: an implication for interaction with Helicobacter pylori.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Jun;295(3):179-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.02.009. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16044857
-
Expression and subcellular distribution of toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection.Clin Exp Immunol. 2004 Jun;136(3):521-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02464.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15147355 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection and eradication on proliferative kinetics of the gastric mucosa].Orv Hetil. 2000 Dec 10;141(50):2695-700. Orv Hetil. 2000. PMID: 11189675 Hungarian.
-
Apoptosis in gastric epithelium induced by Helicobacter pylori infection: implications in gastric carcinogenesis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Jan;96(1):16-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.03447.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001. PMID: 11197247 Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori-induced inflammation and epigenetic changes during gastric carcinogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Dec 7;21(45):12742-56. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i45.12742. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26668499 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association Between IL-4 and IL-6 Expression Variants and Gastric Cancer Among Portuguese Population.GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 4;22(4):143-152. doi: 10.1016/j.jpge.2015.04.001. eCollection 2015 Jul-Aug. GE Port J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 28868397 Free PMC article.
-
Helicobacter pylori-Mediated Immunity and Signaling Transduction in Gastric Cancer.J Clin Med. 2020 Nov 18;9(11):3699. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113699. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33217986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helicobacter pylori DNA promotes cellular proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer by activating toll-like receptor 9.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2019 May-Jun;25(3):181-187. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_309_18. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30618438 Free PMC article.
-
LPS-induced CXCR7 expression promotes gastric Cancer proliferation and migration via the TLR4/MD-2 pathway.Diagn Pathol. 2019 Jan 12;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s13000-019-0780-x. Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30636642 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Helicobacter pylori strains translocate DNA and activate TLR9 via the cancer-associated cag type IV secretion system.Oncogene. 2016 Dec 1;35(48):6262-6269. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.158. Epub 2016 May 9. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 27157617 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suerbaum S, Michetti P. Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1175–1186. - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K, Kaisho T. Toll-like receptors: critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:675–680. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. TLR signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:816–825. - PubMed
-
- Underhill DM, Ozinsky A. Toll-like receptors: key mediators of microbe detection. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14:103–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical