Association of p53 expression with prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 25400812
- PMCID: PMC4230131
Association of p53 expression with prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
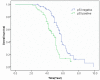
It has been well accepted that p53 overexpression is associated with advanced stages of cancer. However, the prognostic role of p53 overexpression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remains unclear. To investigate the prognostic role of p53 overexpression in patients with ESCC, a retrospective cohort study of 136 ESCC patients was carried out. The expression of p53 protein in tumor tissues was investigated immunohistochemically. Positive expression of p53 protein was detected in 57 ESCC patients (41.9%). The p53 overexpression was associated with smoking (P < 0.001), tumor differentiation (P < 0.001), and tumor size (P < 0.001). In the Kaplan-Meier analysis, patients with p53 overexpression had significantly shorter overall survival than those patients with negative p53 expression (log-rank P < 0.001). Multivariable analysis by Cox regression model further showed that p53 overexpression was a significantly independent predictor of poorer overall survival (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.91; 95% confidence interval [95% CI] 1.03-3.54, P = 0.04). Thus, p53 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with early stage esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and it's a significantly independent predictor of poorer overall survival.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; p53; survival.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KIF-2C expression is correlated with poor prognosis of operable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma male patients.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80493-80507. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11492. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27563815 Free PMC article.
-
Association of p53/p21 expression with cigarette smoking and prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Oct 21;16(39):4958-67. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i39.4958. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20954283 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced stratifin expression can serve as an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Sep;55(9):2552-60. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-1065-0. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Dig Dis Sci. 2010. PMID: 20108042
-
Prognostic significance of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in esophageal carcinoma: a meta-analysis.J BUON. 2013 Apr-Jun;18(2):398-406. J BUON. 2013. PMID: 23818352 Review.
-
P21, COX-2, and E-cadherin are potential prognostic factors for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Feb 1;30(2):1-10. doi: 10.1111/dote.12522. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 27868288 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors associated with the high prevalence of oesophageal cancer in Western Kenya: a review.Infect Agent Cancer. 2017 Nov 3;12:59. doi: 10.1186/s13027-017-0169-y. eCollection 2017. Infect Agent Cancer. 2017. PMID: 29142587 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 overexpression is a prognosticator of poor outcome in esophageal cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Apr;17(4):3826-3834. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10020. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30881503 Free PMC article.
-
Yield of p53 expression in esophageal squamous cell cancer and its relationship with survival.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017 Sep-Oct;23(5):281-286. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_56_17. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28937022 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and molecular bases of esophageal Cancer among Iranians: an update.Diagn Pathol. 2019 Aug 31;14(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13000-019-0875-4. Diagn Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31470870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation on the Potential Correlation Between TP53 and Esophageal Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 27;9:730337. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730337. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34778250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Sharma A, Das BC, Sehgal A, Mehrotra R, Kar P, Sardana S, Phukan R, Mahanta J, Purkayastha J, Saxena S, Kapur S, Chatterjee I, Sharma JK. GSTM1 and GSTT1 polymorphism and susceptibility to esophageal cancer in high- and low-risk regions of India. Tumor Biol. 2013;34:3249–3257. - PubMed
-
- Zhu HC, Yang X, Xu LP, Zhao LJ, Tao GZ, Zhang C, Qin Q, Cai J, Ma JX, Mao WD, Zhang XZ, Cheng HY, Sun XC. Meat consumption is associated with esophageal cancer risk in a meat- and cancer-histological-type dependent manner. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:664–673. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima M, Kato H. Treatment options for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013;14:1345–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous