MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 25400823
- PMCID: PMC4230144
MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
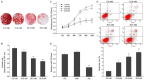
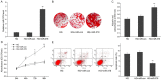
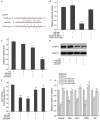
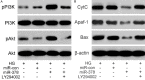
Hyperglycemia is one of the possible causes for osteoporosis and bone fracture in diabetes mellitus. Here we modeled diabetes-induced osteoporosis in vitro using preosteoblastic cell line MC3T3-E1 and a diabetic mice model for in vivo studies. We found that in addition to reducing osteoblast viability and differentiation (mineralization), culture in elevated glucose down regulated microRNA-378 (miR-378) expression but ectopic miR-378 expression reversed the effects of high glucose. We identified caspase-3 (CASP3) as a target of miR-378 and showed that miR-378 repressed CASP3 mRNA and protein expression under high glucose condition. We further showed that both miR-378 expression and CASP3 silencing independently restored alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and the expression of osteoblastic differentiation markers Runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2), osteorix (Osx), collagen I (Col I), osteocalcin (OCN), and osteonectin (ON). We also found that under high glucose conditions miR-378 activated the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and down regulated pro-apoptotic CytC, Apaf-1 and Bax proteins via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Collectively, these results suggest that miR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway.
Keywords: CASP3; MiR-378; PI3K/Akt signaling; high glucose; osteogenic differentiation.
Figures

References
-
- Blakytny R, Spraul M, Jude EB. Review: The diabetic bone: a cellular and molecular perspective. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2011;10:16–32. - PubMed
-
- Bouillon R. Diabetic bone disease. Calcif Tissue Int. 1991;49:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Rakel A, Sheehy O, Rahme E, LeLorier J. Osteoporosis among patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2008;34:193–205. - PubMed
-
- Merlotti D, Gennari L, Dotta F, Lauro D, Nuti R. Mechanisms of impaired bone strength in type 1 and 2 diabetes. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010;20:683–690. - PubMed
-
- Balint E, Szabo P, Marshall CF, Sprague SM. Glucose-induced inhibition of in vitro bone mineralization. Bone. 2001;28:21–28. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
