Full-depth epidermis tomography using a Mirau-based full-field optical coherence tomography
- PMID: 25401013
- PMCID: PMC4230872
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.5.003001
Full-depth epidermis tomography using a Mirau-based full-field optical coherence tomography
Abstract
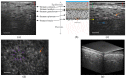
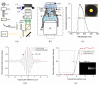
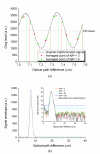
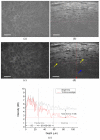
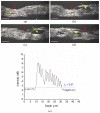
With a Gaussian-like broadband light source from high brightness Ce(3+):YAG single-clad crystal fiber, a full-field optical coherence tomography using a home-designed Mirau objective realized high quality images of in vivo and excised skin tissues. With a 40 × silicone-oil-immersion Mirau objective, the achieved spatial resolutions in axial and lateral directions were 0.9 and 0.51 μm, respectively. Such a high spatial resolution enables the separation of lamellar structure of the full epidermis in both the cross-sectional and en face planes. The number of layers of stratum corneum and its thickness were quantitatively measured. This label free and non-invasive optical probe could be useful for evaluating the water barrier of skin tissue in clinics. As a preliminary in vivo experiment, the blood vessel in dermis was also observed, and the flowing of the red blood cells and location of the melanocyte were traced.
Keywords: (060.2380) Fiber optics sources and detectors; (160.1435) Biomaterials; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.4500) Optical coherence tomography; (180.3170) Interference microscopy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mirau-based line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for three-dimensional high-resolution skin imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Aug;27(8):086002. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.8.086002. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 35962466 Free PMC article.
-
A compact high-speed full-field optical coherence microscope for high-resolution in vivo skin imaging.J Biophotonics. 2019 Feb;12(2):e201800208. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201800208. Epub 2018 Oct 22. J Biophotonics. 2019. PMID: 30062826
-
Full-field optical coherence tomography using immersion Mirau interference microscope.Appl Opt. 2013 Jun 20;52(18):4400-3. doi: 10.1364/AO.52.004400. Appl Opt. 2013. PMID: 23842185
-
Applications of optical coherence tomography in dermatology.J Dermatol Sci. 2005 Nov;40(2):85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2005.07.006. Epub 2005 Aug 31. J Dermatol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16139481 Review.
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation of Augmented Capillary Network Optical Coherence Tomography Image Data of Human Skin for Deep Learning and Capillary Segmentation.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Apr 10;11(4):685. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11040685. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920273 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-mode line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for ultrahigh-resolution vertical and horizontal section imaging of human skin in vivo.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Feb 10;11(3):1327-1335. doi: 10.1364/BOE.385303. eCollection 2020 Mar 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 32206413 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding optical reflectance contrast for real-time characterization of epithelial precursor lesions.Bioeng Transl Med. 2019 Jun 27;4(3):e10137. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10137. eCollection 2019 Sep. Bioeng Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31572795 Free PMC article.
-
Mirau-based line-field confocal optical coherence tomography for three-dimensional high-resolution skin imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Aug;27(8):086002. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.8.086002. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 35962466 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative assessment of in vivo nuclei and layers of human skin by deep learning-based OCT image segmentation.Biomed Opt Express. 2025 Mar 21;16(4):1528-1545. doi: 10.1364/BOE.558675. eCollection 2025 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2025. PMID: 40321995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gambichler T., Boms S., Stücker M., Kreuter A., Moussa G., Sand M., Altmeyer P., Hoffmann K., “Epidermal thickness assessed by optical coherence tomography and routine histology: preliminary results of method comparison,” J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 20(7), 791–795 (2006). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
