The early result of whole pelvic radiotherapy and stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for high-risk localized prostate cancer
- PMID: 25401085
- PMCID: PMC4215618
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00278
The early result of whole pelvic radiotherapy and stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for high-risk localized prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: The rationale for hypofractionated radiotherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer is based on the modern understanding of radiobiology and advances in stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) techniques. Whole-pelvis irradiation combined with SBRT boost for high-risk prostate cancer might escalate biologically effective dose without increasing toxicity. Here, we report our 4-year results of SBRT boost for high-risk localized prostate cancer.
Methods and materials: From October 2009 to August 2012, 41 patients newly diagnosed, high-risk or very high-risk (NCCN definition) localized prostate cancer were treated with whole-pelvis irradiation and SBRT boost. The whole pelvis dose was 45 Gy (25 fractions of 1.8 Gy). The SBRT boost dose was 21 Gy (three fractions of 7 Gy). Ninety percent of these patients received hormone therapy. The toxicities of gastrointestinal (GI) and genitourinary (GU) tracts were scored by Common Toxicity Criteria Adverse Effect (CTCAE v3.0). Biochemical failure was defined by Phoenix definition.
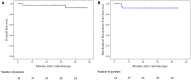
Results: Median follow-up was 42 months. Mean PSA before treatment was 44.18 ng/ml. Mean PSA level at 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24 months was 0.94, 0.44, 0.13, 0.12, and 0.05 ng/ml, respectively. The estimated 4-year biochemical failure-free survival was 91.9%. Three biochemical failures were observed. GI and GU tract toxicities were minimal. No grade 3 acute GU or GI toxicity was noted. During radiation therapy, 27% of the patient had grade 2 acute GU toxicity and 12% had grade 2 acute GI toxicity. At 3 months, most toxicity scores had returned to baseline. At the last follow-up, there was no grade 3 late GU or GI toxicity.
Conclusions: Whole-pelvis irradiation combined with SBRT boost for high-risk localized prostate cancer is feasible with minimal toxicity and encouraging biochemical failure-free survival. Continued accrual and follow-up would be necessary to confirm the biochemical control rate and the toxicity profiles.
Keywords: CyberKnife; Rapidarc; SBRT boost; high-risk prostate cancer; prostate cancer; radiotherapy; stereotactic body; whole-pelvis radiotherapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes of whole pelvis radiotherapy and stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for intermediate- and high-risk prostate cancer.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017 Oct;13(5):e342-e347. doi: 10.1111/ajco.12455. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 26846353
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: Toxicity and Biochemical Disease-Free Outcomes from a Multi-Institutional Patient Registry.Cureus. 2015 Dec 4;7(12):e395. doi: 10.7759/cureus.395. Cureus. 2015. PMID: 26798571 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Pelvic Radiotherapy With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Boost vs. Conventionally Fractionated Radiotherapy for Patients With High or Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 May 29;10:814. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00814. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32547949 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for High-Risk Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;13(4):759. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040759. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pelvic Complications After Prostate Cancer Radiation Therapy and Their Management: An International Collaborative Narrative Review.Eur Urol. 2019 Mar;75(3):464-476. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Eur Urol. 2019. PMID: 30573316
Cited by
-
In silico assessment of the dosimetric quality of a novel, automated radiation treatment planning strategy for linac-based radiosurgery of multiple brain metastases and a comparison with robotic methods.Radiat Oncol. 2018 Mar 15;13(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-0997-y. Radiat Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29544504 Free PMC article.
-
Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy with Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Boost for Unfavorable Prostate Cancer: A Report on 3-Year Toxicity.Front Oncol. 2017 Feb 7;7:5. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00005. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28224113 Free PMC article.
-
High-risk prostate cancer treated with a stereotactic body radiation therapy boost following pelvic nodal irradiation.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 6;14:1325200. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1325200. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38410097 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I/II Study of Extreme Hypofractionated Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Boost to Prostate for Locally Advanced, Node-Positive and Oligometastatic Cancer.Cureus. 2020 Nov 28;12(11):e11751. doi: 10.7759/cureus.11751. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33403181 Free PMC article.
-
Phase I/IIa trial of androgen deprivation therapy, external beam radiotherapy, and stereotactic body radiotherapy boost for high-risk prostate cancer (ADEBAR).Radiat Oncol. 2020 Oct 8;15(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s13014-020-01665-6. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33032643 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; (2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

