Methods of rapid diagnosis for the etiology of meningitis in adults
- PMID: 25402579
- PMCID: PMC4239990
- DOI: 10.2217/bmm.14.67
Methods of rapid diagnosis for the etiology of meningitis in adults
Abstract
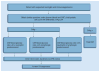
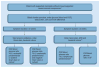
Infectious meningitis may be due to bacterial, mycobacterial, fungal or viral agents. Diagnosis of meningitis must take into account numerous items of patient history and symptomatology along with regional epidemiology and basic cerebrospinal fluid testing (protein, etc.) to allow the clinician to stratify the likelihood of etiology possibilities and rationally select additional diagnostic tests. Culture is the mainstay for diagnosis in many cases, but technology is evolving to provide more rapid, reliable diagnosis. The cryptococcal antigen lateral flow assay (Immuno-Mycologics) has revolutionized diagnosis of cryptococcosis and automated nucleic acid amplification assays hold promise for improving diagnosis of bacterial and mycobacterial meningitis. This review will focus on a holistic approach to diagnosis of meningitis as well as recent technological advances.
Keywords: Cryptococcus meningitis; aseptic meningitis; bacterial meningitis; diagnosis; diagnostic tests; tuberculosis meningitis.
Figures
References
-
- Bhimraj A. Acute community-acquired bacterial meningitis in adults: an evidence-based review. Cleve Clin J Med. 2012;79(6):393–400. - PubMed
-
- Brouwer MC, Thwaites GE, Tunkel AR, van de Beek D. Dilemmas in the diagnosis of acute community-acquired bacterial meningitis. Lancet. 2012;380(9854):1684–1692. - PubMed
-
- Ersoy Y, Yetkin F, Bayraktar MR, Ersoy Y, Yologlu S. A new diagnostic scoring for discrimination of tuberculous and bacterial meningitis on the basis of clinical and laboratory findings. Med Princ Pract. 2012;21(3):259–263. - PubMed
-
- Thigpen MC, Whitney CG, Messonnier NE, et al. Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1998–2007. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(21):2016–2025. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
