Sidestream capnographic monitoring reduces the incidence of arterial oxygen desaturation during propofol ambulatory anesthesia for surgical abortion
- PMID: 25403146
- PMCID: PMC4247237
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.891023
Sidestream capnographic monitoring reduces the incidence of arterial oxygen desaturation during propofol ambulatory anesthesia for surgical abortion
Abstract
Background: This study investigated whether early intervention based on additional use of sidestream capnography could reduce the incidence of oxygen desaturation and hypoxic events in patients receiving propofol anesthesia during surgical abortion.
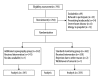
Material/methods: We recruited 704 ASAI-III female patients, 18-52 years old and scheduled for planned painless surgical abortion, and randomized them into a control group (n=359) receiving standard monitoring and an experimental group (n=341) receiving standard monitoring and additional capnography. Exclusion criteria were preexisting cardiovascular disease, preexisting hypotension, bradycardia or arrhythmia, and drug allergy. Anesthesia was induced in all patients with propofol using target-controlled infusion at a target propofol plasma concentration of 4 μg/ml. All patients received flurbiprofen axetil 50 mg and 0.5 μg/kg fentanyl 5 min before anesthesia. Bispectral index was used and maintained between 45 and 60. Main outcome measures were apnea or abnormal ventilation status, rate of oxygen desaturation, occurrence of hypoxia and severe hypoxia, and perioperative side effects.
Results: The experimental group had significantly higher rate of apnea or abnormal ventilation, significantly lower rate of oxygen desaturation, and significant lower occurrence of hypoxia and severe hypoxia compared to the control group. We found no statistically significant differences between the 2 groups in the rates of increased oxygen supplementation, assisted ventilation, bradycardia, hypotension, dosage of atropine, dosage of ephedrine or phenylephrine, and the amount of propofol consumed.
Conclusions: Sidestream capnographic monitoring improves early detection of alterations in ventilation parameters and reduces the incidence of oxygen desaturation and hypoxemia resulting from propofol anesthesia during surgical abortion.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Capnography monitoring in procedural intravenous sedation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2020 Nov;24(11):3761-3770. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03395-1. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Clin Oral Investig. 2020. PMID: 32556657
-
Capnographic monitoring reduces the incidence of arterial oxygen desaturation and hypoxemia during propofol sedation for colonoscopy: a randomized, controlled study (ColoCap Study).Am J Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug;107(8):1205-12. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2012.136. Epub 2012 May 29. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22641306 Clinical Trial.
-
Microstream capnography improves patient monitoring during moderate sedation: a randomized, controlled trial.Pediatrics. 2006 Jun;117(6):e1170-8. doi: 10.1542/peds.2005-1709. Epub 2006 May 15. Pediatrics. 2006. PMID: 16702250 Clinical Trial.
-
Capnographic monitoring of midazolam and propofol sedation during ERCP: a randomized controlled study (EndoBreath Study).Endoscopy. 2016 Jan;48(1):42-50. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1393117. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Endoscopy. 2016. PMID: 26415090 Clinical Trial.
-
Capnographic monitoring of propofol-based sedation during colonoscopy.Endoscopy. 2014 Mar;46(3):236-44. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1359149. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Endoscopy. 2014. PMID: 24338242 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Capnography monitoring in procedural intravenous sedation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Oral Investig. 2020 Nov;24(11):3761-3770. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03395-1. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Clin Oral Investig. 2020. PMID: 32556657
-
The effect of capnography on the incidence of hypoxia during sedation for EGD and colonoscopy in mildly obese patients: a randomized, controlled study.BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 May 31;23(1):188. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02151-8. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37259022 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient safety during procedural sedation using capnography monitoring: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2017 Jun 30;7(6):e013402. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013402. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28667196 Free PMC article.
-
Capnographic monitoring reduces hypoxia incidence in older patients undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy under propofol sedation: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2023 Mar 15;24(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07208-0. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36918924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jones RK, Kavanaugh ML. Changes in abortion rates between 2000 and 2008 and lifetime incidence of abortion. Obstet Gynecol. 2011;117:1358–66. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Y, Gno X, Li Y, et al. Repeat induced abortions and contraceptive practices among unmarried young women seeking an abortion in China. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2004;87:199–202. - PubMed
-
- Gagné A, Guilbert E, Ouellet J, et al. Assessment of pain after elective abortion relating to the use of misoprostol for dilatation of the cervix. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2010;32:244–53. - PubMed
-
- McQuaid KR, Laine L. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials of moderate sedation for routine endoscopic procedures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;67:910–23. - PubMed
-
- Beitz A, Riphaus A, Meining A, et al. Capnographic monitoring reduces the incidence of arterial oxygen desaturation and hypoxemia during propofol sedation for colonoscopy: a randomized, controlled study (ColoCap Study) Am J Gastroenterol. 2012;107:1205–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical