Microarray identification of novel genes downstream of Six1, a critical factor in cranial placode, somite, and kidney development
- PMID: 25403746
- PMCID: PMC4428348
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24229
Microarray identification of novel genes downstream of Six1, a critical factor in cranial placode, somite, and kidney development
Abstract
Background: Six1 plays an important role in the development of several vertebrate organs, including cranial sensory placodes, somites, and kidney. Although Six1 mutations cause one form of branchio-otic syndrome (BOS), the responsible gene in many patients has not been identified; genes that act downstream of Six1 are potential BOS candidates.
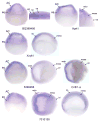
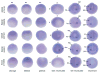
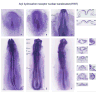
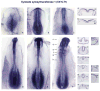
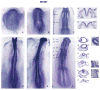
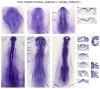
Results: We sought to identify novel genes expressed during placode, somite and kidney development by comparing gene expression between control and Six1-expressing ectodermal explants. The expression patterns of 19 of the significantly up-regulated and 11 of the significantly down-regulated genes were assayed from cleavage to larval stages. A total of 28/30 genes are expressed in the otocyst, a structure that is functionally disrupted in BOS, and 26/30 genes are expressed in the nephric mesoderm, a structure that is functionally disrupted in the related branchio-otic-renal (BOR) syndrome. We also identified the chick homologues of five genes and show that they have conserved expression patterns.
Conclusions: Of the 30 genes selected for expression analyses, all are expressed at many of the developmental times and appropriate tissues to be regulated by Six1. Many have the potential to play a role in the disruption of hearing and kidney function seen in BOS/BOR patients.
Keywords: BOR syndrome; BOS syndrome; cranial ganglia; olfactory; otocyst; pan-placodal region; preplacodal ectoderm.
© 2014 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


















References
-
- Abdelhak S, Kalatzis V, Heilig R, Compain S, Samson D, Vincent C, Weil D, Cruaud C, Sahly I, Leibovici M, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Francis M, Lacombe D, Vigneron J, Charachon R, Boven K, Bedbeder P, Van Regemorter N, Weissenbach J, Petit C. A human homologue of the Drosophila eyes absent gene underlies Branchio–Oto–Renal (BOR) syndrome and identifies a novel gene family. Nature Genet. 1997;15:157–164. - PubMed
-
- Ahrens K, Schlosser G. Tissues and signals involved in the induction of placodal Six1 expression in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 2005;288:40–59. - PubMed
-
- Bailey AP, Streit A. Sensory organs: making and breaking the pre-placodal region. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2006;72:167–204. - PubMed
-
- Bailey AP, Bhattacharyya S, Bronner-Fraser M, Streit A. Lens specification is the ground state of all sensory placodes, from which FGF promotes olfactory identity. Dev Cell. 2006;11:505–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

