Half a century of changing mercury levels in Swedish freshwater fish
- PMID: 25403972
- PMCID: PMC4235934
- DOI: 10.1007/s13280-014-0564-1
Half a century of changing mercury levels in Swedish freshwater fish
Abstract
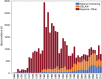
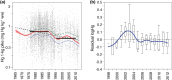
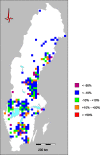
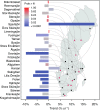
The variability of mercury (Hg) levels in Swedish freshwater fish during almost 50 years was assessed based on a compilation of 44 927 observations from 2881 waters. To obtain comparable values, individual Hg concentrations of fish from any species and of any size were normalized to correspond to a standard 1-kg pike [median: 0.69 mg kg⁻¹ wet weight (ww), mean ± SD: 0.84 ± 0.67 mg kg⁻¹ ww]. The EU Environmental Quality Standard of 0.02 mg kg⁻¹ was exceeded in all waters, while the guideline set by FAO/WHO for Hg levels in fish used for human consumption (0.5-1.0 mg kg⁻¹) was exceeded in 52.5 % of Swedish waters after 2000. Different trend analysis approaches indicated an overall long-term decline of at least 20 % during 1965-2012 but trends did not follow any consistent regional pattern. During the latest decade (2003-2012), however, a spatial gradient has emerged with decreasing trends predominating in southwestern Sweden.
Figures

References
-
- AMAP/UNEP. 2013. Technical Background Report for the Global Mercury Assessment 2013. Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme, Oslo, Norway, vi + 263 pp. Geneva: UNEP Chemicals Branch. Retrieved 7 July, 2014, from http://www.amap.no/documents/doc/technical-background-report-for-the-glo....
-
- Björklund I, Borg H, Johansson K. Mercury in Swedish lakes: Its regional distribution and causes. AMBIO. 1984;13:118–121.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

