Worldwide spread of the Ponseti method for clubfoot
- PMID: 25405086
- PMCID: PMC4133465
- DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v5.i5.585
Worldwide spread of the Ponseti method for clubfoot
Abstract
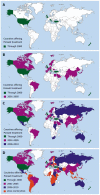
The Ponseti method has become the gold standard for the treatment of idiopathic clubfoot. Its safety and efficacy has been demonstrated extensively in the literature, leading to increased use around the world over the last two decades. This has been demonstrated by the increase in Ponseti related PubMed publications from many countries. We found evidence of Ponseti activity in 113 of 193 United Nations members. The contribution of many organizations which provide resources to healthcare practitioners in low and middle income countries, as well as Ponseti champions and modern communication technology, have helped to spread the Ponseti method around the world. Despite this, there are many countries where the Ponseti method is not being used, as well as many large countries in which the extent of activity is unknown. With its low rate of complication, low cost, and high effectiveness, this method has unlimited potential to treat clubfoot in both developed and undeveloped countries. Our listing of countries who have not yet shown presence of Ponseti activity will help non-governmental organizations to target those countries which still need the most help.
Keywords: Children; Clubfoot; Organization; Ponseti; World.
Figures

References
-
- Laaveg SJ, Ponseti IV. Long-term results of treatment of congenital club foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C. Long-term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A:1286–1294. - PubMed
-
- Dobbs MB, Nunley R, Schoenecker PL. Long-term follow-up of patients with clubfeet treated with extensive soft-tissue release. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:986–996. - PubMed
-
- Abdelgawad AA, Lehman WB, van Bosse HJ, Scher DM, Sala DA. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot using the Ponseti method: minimum 2-year follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2007;16:98–105. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

