Effects of estrogen and venlafaxine on menopause-related quality of life in healthy postmenopausal women with hot flashes: a placebo-controlled randomized trial
- PMID: 25405571
- PMCID: PMC4610378
- DOI: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000364
Effects of estrogen and venlafaxine on menopause-related quality of life in healthy postmenopausal women with hot flashes: a placebo-controlled randomized trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the effects of low-dose estradiol (E2) or venlafaxine on menopause-related quality of life and associated symptoms in healthy perimenopausal and postmenopausal women with hot flashes.
Methods: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of low-dose oral 17β-E2 0.5 mg/day and venlafaxine XR 75 mg/day, versus identical placebo, was conducted among 339 women (aged 40-62 y) experiencing two or more vasomotor symptoms (VMS) per day (mean [SD], 8.07 [5.29]) who were recruited at three clinical sites from November 2011 to October 2012. The primary trial outcome, as reported previously, was frequency of VMS at 8 weeks. Here, we report on secondary endpoints of total and domain scores from the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire (MENQOL) and from measures of pain (Pain, Enjoyment in life, and General activity scale), depression (Patient Health Questionnaire-9), anxiety (Generalized Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire-7), and perceived stress (Perceived Stress Scale).
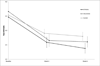
Results: Treatment with both E2 and venlafaxine resulted in significantly greater improvement in quality of life, as measured by total MENQOL scores, compared with placebo (E2: mean difference at 8 wk, -0.4; 95% CI, -0.7 to -0.2; P < 0.001; venlafaxine: mean difference at 8 wk, -0.2; 95% CI, -0.5 to 0.0; P = 0.04). Quality-of-life domain analyses revealed that E2 had beneficial treatment effects on all domains of the MENQOL except for the psychosocial domain, whereas venlafaxine benefits were observed only in the psychosocial domain. Neither E2 nor venlafaxine improved pain, anxiety, or depressive symptoms, although baseline symptom levels were low. Modest benefits were observed for perceived stress with venlafaxine.
Conclusions: Both low-dose E2 and venlafaxine are effective pharmacologic agents for improving menopause-related quality of life in healthy women with VMS.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01418209.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial disclosures/conflicts of interest: No conflicts reported for any other authors.
Figures
Comment in
-
Antidepressants decrease hot flashes and improve life quality.Menopause. 2015 Jun;22(6):587-8. doi: 10.1097/GME.0000000000000449. Menopause. 2015. PMID: 25756695 No abstract available.
References
-
- Williams RE, Kalilani L, DiBenedetti DB, et al. Frequency and severity of vasomotor symptoms among peri- and postmenopausal women in the United States. Climacteric. 2008 Feb;11(1):32–43. - PubMed
-
- Williams RE, Levine KB, Kalilani L, Lewis J, Clark RV. Menopause-specific questionnaire assessment in US population-based study shows negative impact on health-related quality of life. Maturitas. 2009 Feb 20;62(2):153–159. - PubMed
-
- Williams RE, Kalilani L, DiBenedetti DB, Zhou X, Fehnel SE, Clark RV. Healthcare seeking and treatment for menopausal symptoms in the United States. Maturitas. 2007 Dec 20;58(4):348–358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01AG032659/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032682/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032669/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032659/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032699/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG048209/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032700/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032699/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032669/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032656/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG032700/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01AG032682/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

