In vitro growth of Plasmodium falciparum in neonatal blood
- PMID: 25406504
- PMCID: PMC4242501
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-436
In vitro growth of Plasmodium falciparum in neonatal blood
Abstract
Background: Children below the age of six months suffer less often from malaria than older children in sub-Saharan Africa. This observation is commonly attributed to the persistence of foetal haemoglobin (HbF), which is considered not to permit growth of Plasmodium falciparum and therefore providing protection against malaria. Since this concept has recently been challenged, this study evaluated the effect of HbF erythrocytes and maternal plasma on in vitro parasite growth of P. falciparum in Central African Gabon.
Methods: Umbilical cord blood and peripheral maternal blood were collected at delivery at the Albert Schweitzer Hospital in Gabon. Respective erythrocyte suspension and plasma were used in parallel for in vitro culture. In vitro growth rates were compared between cultures supplemented with either maternal or cord erythrocytes. Plasma of maternal blood and cord blood was evaluated. Parasite growth rates were assessed by the standard HRP2-assay evaluating the increase of HRP2 concentration in Plasmodium culture.
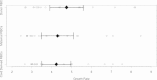
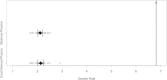
Results: Culture of P. falciparum using foetal erythrocytes led to comparable growth rates (mean growth rate = 4.2, 95% CI: 3.5 - 5.0) as cultures with maternal red blood cells (mean growth rate =4.2, 95% CI: 3.4 - 5.0) and those from non-malaria exposed individuals (mean growth rate = 4.6, 95% CI: 3.8 - 5.5). Standard in vitro culture of P. falciparum supplemented with either maternal or foetal plasma showed both significantly lower growth rates than a positive control using non-malaria exposed donor plasma.
Conclusions: These data challenge the concept of HbF serving as intrinsic inhibitor of P. falciparum growth in the first months of life. Erythrocytes containing HbF are equally permissive to P. falciparum growth in vitro. However, addition of maternal and cord plasma led to reduced in vitro growth which may translate to protection against clinical disease or show synergistic effects with HbF in vivo. Further studies are needed to elucidate the pathophysiology of innate and acquired protection against neonatal malaria.
Figures

References
-
- WHO . World Malaria Report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Klein Klouwenberg PMC, Oyakhirome S, Schwarz NG, Gläser B, Issifou S, Kiessling G, Klöpfer A, Kremsner PG, Längin M, Lassmann B, Necek M, Pötschke M, Ritz A, Grobusch MP. Malaria and asymptomatic parasitaemia in Gabonese infants under the age of 3 months. Acta Trop. 2005;95:81–85. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramharter M, Schuster K, Bouyou-Akotet MK, Adgenika AA, Schmits K, Mombo-Ngoma G, Agnandji ST, Nemeth J, Afène SN, Issifou S, Onnas IN, Kombila M, Kremsner PG. Malaria in pregnancy before and after the implementation of a national IPTp program in Gabon. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77:418–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

