Ethnic differences in timely adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy for breast cancer in New Zealand: a cohort study
- PMID: 25406582
- PMCID: PMC4242494
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-839
Ethnic differences in timely adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy for breast cancer in New Zealand: a cohort study
Abstract
Background: Indigenous and/or minority ethnic women are known to experience longer delays for treatment of breast cancer, which has been shown to contribute to ethnic inequities in breast cancer mortality. We examined factors associated with delay in adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy for breast cancer, and its impact on the mortality inequity between Indigenous Māori and European women in New Zealand.
Methods: All women with newly diagnosed invasive non-metastatic breast cancer diagnosed during 1999-2012, who underwent adjuvant chemotherapy (n = 922) or radiation therapy (n = 996) as first adjuvant therapy after surgery were identified from the Waikato breast cancer register. Factors associated with delay in adjuvant chemotherapy (60-day threshold) and radiation therapy (90-day threshold) were analysed in univariate and multivariate models. Association between delay in adjuvant therapy and breast cancer mortality were explored in Cox regression models.
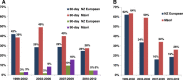
Results: Overall, 32.4% and 32.3% women experienced delays longer than thresholds for chemotherapy and radiotherapy, respectively. Higher proportions of Māori compared with NZ European women experienced delays longer than thresholds for adjuvant radiation therapy (39.8% vs. 30.6%, p = 0.045) and chemotherapy (37.3% vs. 30.5%, p = 0.103). Rural compared with urban residency, requiring a surgical re-excision and treatment in public compared with private hospitals were associated with significantly longer delays (p < 0.05) for adjuvant therapy in the multivariate model. Breast cancer mortality was significantly higher for women with a delay in initiating first adjuvant therapy (hazard ratio [HR] =1.45, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.05-2.01). Mortality risks were higher for women with delays in chemotherapy (HR = 1.34, 95% CI 0.89-2.01) or radiation therapy (HR = 1.28, 95% CI 0.68-2.40), although these were statistically non-significant.
Conclusions: Indigenous Māori women appeared to experience longer delays for adjuvant breast cancer treatment, which may be contributing towards higher breast cancer mortality in Māori compared with NZ European women. Measures to reduce delay in adjuvant therapy may reduce ethnic inequities and improve breast cancer outcomes for all women with breast cancer in New Zealand.
Figures
References
-
- Gwyn K, Bondy ML, Cohen DS, Lund MJ, Liff JM, Flagg EW, Brinton LA, Eley JW, Coates RJ. Racial differences in diagnosis, treatment, and clinical delays in a population-based study of patients with newly diagnosed breast carcinoma. Cancer. 2004;100(8):1595–1604. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20169. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/839/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical