Changes in thrombin generation and D-dimer concentrations in women injecting enoxaparin during pregnancy and the puerperium
- PMID: 25406658
- PMCID: PMC4240885
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-014-0384-0
Changes in thrombin generation and D-dimer concentrations in women injecting enoxaparin during pregnancy and the puerperium
Abstract
Background: It is well accepted that the gravid state is hypercoagulable and a significant cause of both maternal morbidity and mortality in the Western world. Although thrombin generation is reported to be increased in pregnant women, uncertainty exists on the pattern of thrombin generation change during this time. The aim of this study is to describe thrombin generation changes and D-dimer concentrations in women injecting enoxaparin during pregnancy the postnatal period.
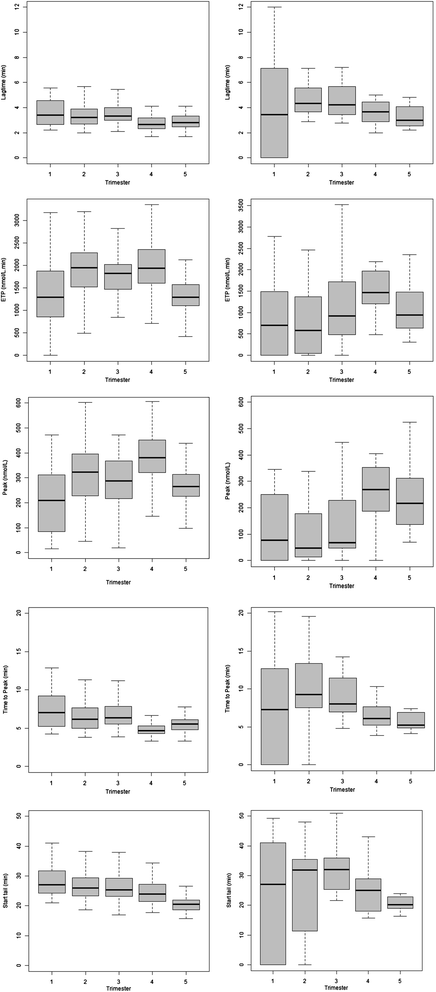
Methods: One hundred and twenty-three women injecting enoxaparin had their thrombin generation, as measured by Calibrated Automated Thombinography (CAT), repeatedly assayed during pregnancy, once in each trimester, at delivery and 8 weeks post-partum. Furthermore, to understand the impact enoxaparin has on D-dimer concentrations during pregnancy, D-dimer concentrations were measured monthly in the recruited women.
Results: Thrombin generation was found to increase in the first trimester (mean endogenous thrombin potential (ETP): 1391 nmol/L.min), further increasing during the second trimester (mean ETP: 1757 nmol/L.min), after which it plateaued through to delivery, where it peaked (mean ETP: 1857 nmol/L.min) and then fell back at 8 weeks post-partum (ETP: 1293 nmol/L.min). In contrast D-dimer concentrations increased exponentially during the antenatal period, despite the enoxaparin prescription.
Conclusion: Our results provide further evidence on alterations of thrombin generation during pregnancy and the postnatal period.
Figures
References
-
- Fritsch P, Kleber M, Rosenkranz A, Fritsch M, Muntean W, Mangge H, Reinehr T. Haemostatic alterations in overweight children: Associations between metabolic syndrome, thrombin generation, and fibrinogen levels. Atherosclerosis. 2010;212:650–655. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.06.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tchaikovski SN, van Vliet HA, Thomassen MC, Bertina RM, Rosendaal FR, Sandset PM, Helmerhorst FM, Tans G, Rosing J. Effect of oral contraceptives on thrombin generation measured via calibrated automated thrombography. Thromb Haemost. 2007;98:1350–1356. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous