Current knowledge on HIV-associated Plasmablastic Lymphoma
- PMID: 25408850
- PMCID: PMC4235470
- DOI: 10.4084/MJHID.2014.064
Current knowledge on HIV-associated Plasmablastic Lymphoma
Abstract
HIV-associated PBL is an AIDS-defining cancer, classified by WHO as a distinct entity of aggressive DLBCL. To date less than 250 cases have been published, of them 17 are pediatric. The pathogenesis of this rare disease is related to immunodeficiency, chronic immune stimulation and EBV. Clinically is a rapid growing destructive disease mainly involving the oral cavity even if extraoral and extranodal sites are not infrequent. The diagnosis requires tissue mass or lymph node biopsy and core needle or fine needle biopsy is acceptable only for difficult access sites. Classically immunophenotype is CD45, CD20, CD79a negative and CD38, CD138, MUM1 positive, EBER and KI67 is >80%. Regarding the therapy, standard treatment is, usually, CHOP or CHOP-like regimens while more intensive regimens as CODOX-M/IVAC or DA-EPOCH are possible options. Use of cART is recommended during chemotherapy, keeping in mind the possible overlapping toxicities. Rituximab is not useful for this CD20 negative disease and CNS prophylaxis is mandatory. Intensification with ABMT in CR1 may be considered for fit patients. For refractory/relapsed patients, therapy is, usually, considered palliative, however, in chemo-sensitive disease, intensification + ABMT or new drugs as Bortezomib may be considered. Factors affecting outcome are achieving complete remission, PS, clinical stage, MYC, IPI score. Reported median PFS ranges between 6-7 months and median OS ranges between 11-13 months. Long term survivors are reported but mostly in pediatric patients. Finally, due to the scarcity of data on this subtype of NHL we suggest that the diagnosis and the management of HIV-positive PBL patients should be performed in specialized centers.
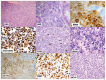
Figures
References
-
- Stein H, Dallenbach F. In: Neoplastic Hematopathology. Knowles DM, editor. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore, MA: 1992. pp. 675–714.
-
- Delecluse HJ, Anagnostopoulos I, Dallenbach F, et al. Plasmablastic lymphomas of the oral cavity: a new entity associated with the human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 1997;89:1413–1420. - PubMed
-
- Stein H, Harris N, Campo E. Plasmablastic lymphoma. In: Swerdlow S, Campo E, Harris N, et al., editors. WHO Classification of Tumors of the Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 4th ed. Lyon, France: IARC; 2008. pp. P256–257.
-
- Morscio J, Dierickx D, Verhoef G, et al. Clinopathologic comparison of Plasmablastic lymphoma in HIV-positive, immunocompetent, and posttransplant patients: Single-center series of 25 Cases and Meta-analysis of 277 reported cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014 Jul;38(7):875–86. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

