Ionizing radiation sensitizes breast cancer cells to Bcl-2 inhibitor, ABT-737, through regulating Mcl-1
- PMID: 25409124
- PMCID: PMC5523983
- DOI: 10.1667/RR13856.1
Ionizing radiation sensitizes breast cancer cells to Bcl-2 inhibitor, ABT-737, through regulating Mcl-1
Abstract
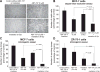
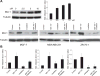
Breast-conserving surgery followed by radiation therapy has become the standard of care for early stage breast cancer. However, there are some patients that develop a local failure. We have previously shown that Bcl-2 overexpression was associated with an increased risk of local recurrence in patients with early stage breast cancer. The purpose of this study was to explore an approach to overcome radiation resistance by targeting pro-survival Bcl-2 family proteins in breast cancer cells. The breast cancer cell lines MCF-7, ZR-75-1 and MDA-MB231 were used in this study. siRNAs were employed to silence myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1). A small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, ABT-737, was used to target anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins. Apoptosis was identified by FITC Annexin V, PI staining and Western blot analysis. The sensitivity to ionizing radiation and ABT-737 were measured by clonogenic assays. The effect of radiation and ABT-737 was also tested in a MCF-7 xenograft mouse model. Our data demonstrate that the combination of ABT-737 and radiation-induced apoptosis had an inhibitory effect on breast cancer cell proliferation. However, treatment with ABT-737 resulted in elevated Mcl-1 in breast cancer cell lines. Targeting Mcl-1 by siRNA sensitized MCF-7 cells to ABT-737. We revealed that radiation blunted Mcl-1 elevation induced by ABT-737, and that radiation downregulated Mcl-1 by promoting its degradation. Our results indicate that radiation and ABT-737 exert a synergistic effect on breast cancer cell lines through downregulating Mcl-1 and activating the bak-apoptotic pathway. These results support the combination of radiation and pro-survival Bcl-2 family inhibitor as a potential novel therapeutic strategy in the local-regional management of breast cancer.
Figures




References
-
- Fisher B, Jeong JH, Anderson S, Bryant J, Fisher ER, Wolmark N. Twenty-five-year follow-up of a randomized trial comparing radical mastectomy, total mastectomy, and total mastectomy followed by irradiation. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:567–75. - PubMed
-
- Haffty BG, Carter D, Flynn SD, Fischer DB, Brash DE, Simons J, et al. Local recurrence versus new primary: clinical analysis of 82 breast relapses and potential applications for genetic fingerprinting. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1993;27:575–83. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Anderson S, Fisher ER, Redmond C, Wickerham DL, Wolmark N, et al. Significance of ipsilateral breast tumour recurrence after lumpectomy. Lancet. 1991;338:327–31. - PubMed
-
- Balcer-Kubiczek EK. Apoptosis in radiation therapy: a double-edged sword. Exp Oncol. 2012;34:277–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

