An ERK/Cdk5 axis controls the diabetogenic actions of PPARγ
- PMID: 25409143
- PMCID: PMC4297557
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13887
An ERK/Cdk5 axis controls the diabetogenic actions of PPARγ
Abstract
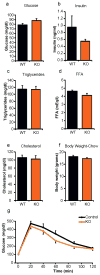
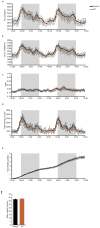
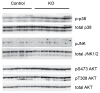
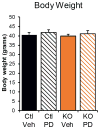
Obesity-linked insulin resistance is a major precursor to the development of type 2 diabetes. Previous work has shown that phosphorylation of PPARγ (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ) at serine 273 by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) stimulates diabetogenic gene expression in adipose tissues. Inhibition of this modification is a key therapeutic mechanism for anti-diabetic drugs that bind PPARγ, such as the thiazolidinediones and PPARγ partial agonists or non-agonists. For a better understanding of the importance of this obesity-linked PPARγ phosphorylation, we created mice that ablated Cdk5 specifically in adipose tissues. These mice have both a paradoxical increase in PPARγ phosphorylation at serine 273 and worsened insulin resistance. Unbiased proteomic studies show that extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinases are activated in these knockout animals. Here we show that ERK directly phosphorylates serine 273 of PPARγ in a robust manner and that Cdk5 suppresses ERKs through direct action on a novel site in MAP kinase/ERK kinase (MEK). Importantly, pharmacological inhibition of MEK and ERK markedly improves insulin resistance in both obese wild-type and ob/ob mice, and also completely reverses the deleterious effects of the Cdk5 ablation. These data show that an ERK/Cdk5 axis controls PPARγ function and suggest that MEK/ERK inhibitors may hold promise for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Figures

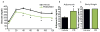
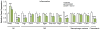

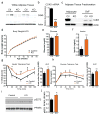
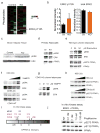
Similar articles
-
Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5.Nature. 2010 Jul 22;466(7305):451-6. doi: 10.1038/nature09291. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20651683 Free PMC article.
-
A novel non-agonist peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) ligand UHC1 blocks PPARγ phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) and improves insulin sensitivity.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 19;289(38):26618-26629. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.566794. Epub 2014 Aug 6. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25100724 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic hedgehog signaling instigates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance by targeting PPARγ stability.J Biol Chem. 2019 Mar 1;294(9):3284-3293. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004411. Epub 2018 Dec 20. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30573683 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling a master switch of adipocyte development and insulin sensitivity: covalent modifications of PPARγ.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jul;1822(7):1090-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.03.014. Epub 2012 Apr 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22504298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of PPARgamma activity during adipogenesis.Int J Obes (Lond). 2005 Mar;29 Suppl 1:S13-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802907. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005. PMID: 15711576 Review.
Cited by
-
The PPAR Ω Pocket: Renewed Opportunities for Drug Development.PPAR Res. 2020 Jul 1;2020:9657380. doi: 10.1155/2020/9657380. eCollection 2020. PPAR Res. 2020. PMID: 32695150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pleiotropic Actions of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Dysregulated Metabolic Homeostasis, Inflammation and Cancer: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 24;17(7):999. doi: 10.3390/ijms17070999. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27347932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the Mouse a Good Model of Human PPARγ-Related Metabolic Diseases?Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 30;17(8):1236. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081236. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27483259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PPARγ in chemotherapy-evoked pain.Neurosci Lett. 2021 May 14;753:135845. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.135845. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Neurosci Lett. 2021. PMID: 33774149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inactivation of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5 in Hair Cells Causes Hearing Loss in Mice.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Dec 11;11:461. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00461. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30618612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu JG, et al. The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 2002;51:2968–2974. - PubMed
-
- Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPARγ2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 1994;79:1147–1156. - PubMed
-
- Chawla A, Schwarz EJ, Dimaculangan DD, Lazar MA. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma: adipose-predominant expression and induction early in adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology. 1994;135:798–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

