Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibits thapsigargin-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 25409163
- PMCID: PMC4237446
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113499
Hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A inhibits thapsigargin-induced apoptosis
Abstract
Background: We previously reported that the hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) down-regulates TLR4 signaling and lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of hepatocytes. There have been several reports regarding the association between HCV infection and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Here, we examined the regulation of HCV NS5A on the apoptosis of hepatocytes induced by thapsigargin, an inducer of ER stress.
Methods: The apoptotic response to thapsigargin and the expression of molecules involved in human hepatocyte apoptotic pathways were examined in the presence or absence of HCV NS5A expression.
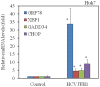
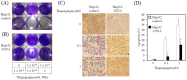
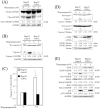
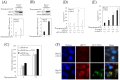
Results: HCV JFH1 infection induced ER stress in the Huh7 cell line. HCV NS5A protected HepG2 cells against thapsigargin-induced apoptosis, the effect of which was linked to the enhanced expression of the 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein/immunoglobulin heavy-chain binding protein (GRP78). Consistent with a conferred pro-survival advantage, HCV NS5A reduced poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase cleavage and activation of caspases-3, -7 and -9, and Bax expression, while increasing the expressions of the anti-apoptotic molecules XIAP and c-FLIP. HCV NS5A weakly interacts with GRP78 and enhances GRP78 expression in hepatocytes.
Conclusion: HCV NS5A enhances GRP78 expression, resulting in the inhibition of apoptotic properties, and inhibits thapsigargin-induced apoptotic pathways in human hepatocytes, suggesting that disruption of ER stress-mediated apoptosis may have a role in the pathogenesis of HCV infection. Thus, HCV NS5A might engender the survival of HCV-infected hepatocytes contributing to the establishment of persistent infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Simmonds P (2001) The origin and evolution of hepatitis viruses in humans. J Gen Virol 82: 693–712 PubMed: 11257174 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

