Berberine improves kidney function in diabetic mice via AMPK activation
- PMID: 25409232
- PMCID: PMC4237447
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113398
Berberine improves kidney function in diabetic mice via AMPK activation
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Berberine Improves Kidney Function in Diabetic Mice via AMPK Activation.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 28;12(12):e0190562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190562. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29284063 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
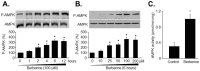
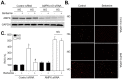
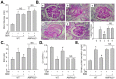
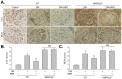
Diabetic nephropathy is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. Effective therapies to prevent the development of this disease are required. Berberine (BBR) has several preventive effects on diabetes and its complications. However, the molecular mechanism of BBR on kidney function in diabetes is not well defined. Here, we reported that activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is required for BBR-induced improvement of kidney function in vivo. AMPK phosphorylation and activity, productions of reactive oxygen species (ROS), kidney function including serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine clearance (Ccr), and urinary protein excretion, morphology of glomerulus were determined in vitro or in vivo. Exposure of cultured human glomerulus mesangial cells (HGMCs) to BBR time- or dose-dependently activates AMPK by increasing the thr172 phosphorylation and its activities. Inhibition of LKB1 by siRNA or mutant abolished BBR-induced AMPK activation. Incubation of cells with high glucose (HG, 30 mM) markedly induced the oxidative stress of HGMCs, which were abolished by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside, AMPK gene overexpression or BBR. Importantly, the effects induced by BBR were bypassed by AMPK siRNA transfection in HG-treated HGMCs. In animal studies, streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia dramatically promoted glomerulosclerosis and impaired kidney function by increasing serum BUN, urinary protein excretion, and decreasing Ccr, as well as increased oxidative stress. Administration of BBR remarkably improved kidney function in wildtype mice but not in AMPKα2-deficient mice. We conclude that AMPK activation is required for BBR to improve kidney function in diabetic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, et al. (2005) The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care 28: 2130–2135. - PubMed
-
- Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, et al. (2004) Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care 27 Suppl 1: S79–83. - PubMed
-
- Jha JC, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Cooper ME (2014) New Insights Into the Use of Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 21: 318–326. - PubMed
-
- Forbes JM, Coughlan MT, Cooper ME (2008) Oxidative stress as a major culprit in kidney disease in diabetes. Diabetes 57: 1446–1454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

