Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement
- PMID: 25409509
- PMCID: PMC4237348
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112963
Pilon: an integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement
Abstract
Advances in modern sequencing technologies allow us to generate sufficient data to analyze hundreds of bacterial genomes from a single machine in a single day. This potential for sequencing massive numbers of genomes calls for fully automated methods to produce high-quality assemblies and variant calls. We introduce Pilon, a fully automated, all-in-one tool for correcting draft assemblies and calling sequence variants of multiple sizes, including very large insertions and deletions. Pilon works with many types of sequence data, but is particularly strong when supplied with paired end data from two Illumina libraries with small e.g., 180 bp and large e.g., 3-5 Kb inserts. Pilon significantly improves draft genome assemblies by correcting bases, fixing mis-assemblies and filling gaps. For both haploid and diploid genomes, Pilon produces more contiguous genomes with fewer errors, enabling identification of more biologically relevant genes. Furthermore, Pilon identifies small variants with high accuracy as compared to state-of-the-art tools and is unique in its ability to accurately identify large sequence variants including duplications and resolve large insertions. Pilon is being used to improve the assemblies of thousands of new genomes and to identify variants from thousands of clinically relevant bacterial strains. Pilon is freely available as open source software.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

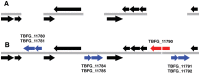
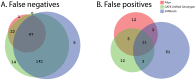
References
-
- Chewapreecha C, Harris SR, Croucher NJ, Turner C, Marttinen P, et al. (2014) Dense genomic sampling identifies highways of pneumococcal recombination. Nat Genet 46: 305–309 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24509479 Accessed 21 March 2014.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Comas I, Coscolla M, Luo T, Borrell S, Holt KE, et al. (2013) Out-of-Africa migration and Neolithic coexpansion of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with modern humans. Nat Genet 45: 1176–1182 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23995134 Accessed 19 March 2014.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Croucher NJ, Finkelstein J a, Pelton SI, Mitchell PK, Lee GM, et al. (2013) Population genomics of post-vaccine changes in pneumococcal epidemiology. Nat Genet 45: 656–663 Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3725542&tool=p... Accessed 21 March 2014.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grad YH, Kirkcaldy RD, Trees D, Dordel J, Harris SR, et al. (2014) Genomic epidemiology of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with reduced susceptibility to cefixime in the USA: a retrospective observational study. Lancet Infect Dis 14: 220–226 Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24462211 Accessed 21 March 2014.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ronen R, Boucher C, Chitsaz H, Pevzner P (2012) SEQuel: improving the accuracy of genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 28: i188–96 Available: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=3371851&tool=p... Accessed 20 January 2014.. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

