Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation delays tumor progression and prolongs overall survival in patients with intermediate (BCLC B) hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25409554
- PMCID: PMC4256894
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-849
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization combined with radiofrequency ablation delays tumor progression and prolongs overall survival in patients with intermediate (BCLC B) hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: This study was designed to evaluate the effectiveness of radiofrequency ablation in patients with intermediate (BCLC B) stage hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent transcatheter arterial chemoembolization.
Methods: Included in this study were 211 patients with intermediate stage HCC who underwent initial transcatheter arterial chemoembolization and were potentially amendable for radiofrequency ablation (single tumor with diameter 5-8 cm, median 6.0 cm; 2-5 multiple nodules with diameter less than 5 cm) between January 2005 and December 2011. According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 55 patients were treated with following radiofrequency ablation, and the remaining 156 patients were treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone. The treatment effectiveness, local tumor control and survival outcome between the two groups were compared.
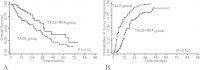
Results: The complete tumor necrosis rate after treatment was 76.9% in combination group vs. 46.5% in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone group (P = 0.02). The major complication rate was 1.8% in combination group vs. 2.6% in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone group. Follow-up observation showed that the total tumor control rate was 74.5% in combination group versus 54.5% in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization alone group (P < 0.001). The 1-, 3- and 5-year survival rates in combination group were significantly higher than those in TACE alone group (P = 0.01).
Conclusions: Radiofrequency ablation following initial transcatheter arterial chemoembolization delays tumor progression and prolongs overall survival of patients with intermediate stage HCC tumors.
Figures
References
-
- Benson AB, 3rd, Abrams TA, Ben-Josef E, Bloomston PM, Botha JF, Clary BM, Covey A, Curley SA, D'Angelica MI, Davila R, Ensminger WD, Gibbs JF, Laheru D, Malafa MP, Marrero J, Meranze SG, Mulvihill SJ, Park JO, Posey JA, Sachdev J, Salem R, Sigurdson ER, Sofocleous C, Vauthey JN, Venook AP, Goff LW, Yen Y, Zhu AX. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: hepatobiliary cancers. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2009;7:350–391. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Omata M, Lesmana LA, Tateishi R, Chen PJ, Lin SM, Yoshida H, Kudo M, Lee JM, Choi BI, Poon RT, Shiina S, Cheng AL, Jia JD, Obi S, Han KH, Jafri W, Chow P, Lim SG, Chawla YK, Budihusodo U, Gani RA, Lesmana CR, Putranto TA, Liaw YF, Sarin SK. Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver consensus recommendations on hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2010;4:439–474. doi: 10.1007/s12072-010-9165-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Real MI, Montaña X, Planas R, Coll S, Aponte J, Ayuso C, Sala M, Muchart J, Solà R, Rodés J, Bruix J, Barcelona Liver Cancer Group. Liver Unit, Digestive Disease Institute, Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1734–1739. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08649-X. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here:http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2407/14/849/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

