Principles of regulatory information conservation between mouse and human
- PMID: 25409826
- PMCID: PMC4343047
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13985
Principles of regulatory information conservation between mouse and human
Abstract
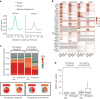
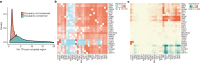
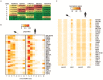
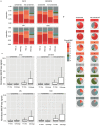
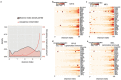
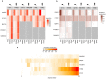
To broaden our understanding of the evolution of gene regulation mechanisms, we generated occupancy profiles for 34 orthologous transcription factors (TFs) in human-mouse erythroid progenitor, lymphoblast and embryonic stem-cell lines. By combining the genome-wide transcription factor occupancy repertoires, associated epigenetic signals, and co-association patterns, here we deduce several evolutionary principles of gene regulatory features operating since the mouse and human lineages diverged. The genomic distribution profiles, primary binding motifs, chromatin states, and DNA methylation preferences are well conserved for TF-occupied sequences. However, the extent to which orthologous DNA segments are bound by orthologous TFs varies both among TFs and with genomic location: binding at promoters is more highly conserved than binding at distal elements. Notably, occupancy-conserved TF-occupied sequences tend to be pleiotropic; they function in several tissues and also co-associate with many TFs. Single nucleotide variants at sites with potential regulatory functions are enriched in occupancy-conserved TF-occupied sequences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA113275/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 3RC2HG005602/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG007004/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006996/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004037/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005573/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HG007356/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK065806/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007175/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE024427/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 5U54HG006996/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U41 HG007234/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006997/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK044746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065806/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES024992/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54HG00699/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006997/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 HG005602/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- RC2HG005573/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY021482/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG007354/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006998/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

