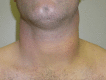
Traumatic rupture of sternocleidomastoid muscle following an epileptic seizure
- PMID: 25410030
- PMCID: PMC4244323
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205531
Traumatic rupture of sternocleidomastoid muscle following an epileptic seizure
Abstract
A 29-year-old man, a known epileptic, presented to an accident and emergency department following a tonic-clonic seizure, suffering a second seizure in the department. Subsequently, he reported neck pain, swelling and stiffness. An otorhinolaryngology neck examination revealed a tender left side with two palpable masses and a reduced range of movement. Ultrasound confirmed a ruptured middle third of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle, which was successfully treated non-surgically with analgaesia and intensive physiotherapy. Uncommonly, sternocleidomastoid muscle rupture has been reported following high-velocity trauma, but to the best of our knowledge this is the first case described in the literature following an epileptic seizure.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Lee IJ, Lim SY, Song HS et al. . Complete tight fibrous band release and resection in congenital muscular torticollis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2010;63: 947–53. - PubMed
-
- Schuyler-Hacker H, Green R, Wingate L et al. . Acute torticollis secondary to rupture of the sternocleidomastoid. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 1989;70:851–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical