T1 mapping and survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis
- PMID: 25411195
- PMCID: PMC4301598
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu444
T1 mapping and survival in systemic light-chain amyloidosis
Abstract
Aims: To assess the prognostic value of myocardial pre-contrast T1 and extracellular volume (ECV) in systemic amyloid light-chain (AL) amyloidosis using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) T1 mapping.
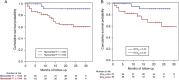
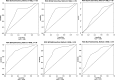
Methods and results: One hundred patients underwent CMR and T1 mapping pre- and post-contrast. Myocardial ECV was calculated at contrast equilibrium (ECV(i)) and 15 min post-bolus (ECVb). Fifty-four healthy volunteers served as controls. Patients were followed up for a median duration of 23 months and survival analyses were performed. Mean ECV(i) was raised in amyloid (0.44 ± 0.12) as was ECV(b) (mean 0.44 ± 0.12) compared with healthy volunteers (0.25 ± 0.02), P < 0.001. Native pre-contrast T1 was raised in amyloid (mean 1080 ± 87 ms vs. 954 ± 34 ms, P < 0.001). All three correlated with pre-test probability of cardiac involvement, cardiac biomarkers, and systolic and diastolic dysfunction. During follow-up, 25 deaths occurred. An ECV(i) of >0.45 carried a hazard ratio (HR) for death of 3.84 [95% confidence interval (CI): 1.53-9.61], P = 0.004 and pre-contrast T1 of >1044 ms = HR 5.39 (95% CI: 1.24-23.4), P = 0.02. Extracellular volume after primed infusion and ECVb performed similarly. Isolated post-contrast T1 was non-predictive. In Cox regression models, ECV(i) was independently predictive of mortality (HR = 4.41, 95% CI: 1.35-14.4) after adjusting for E:E', ejection fraction, diastolic dysfunction grade, and NT-proBNP.
Conclusion: Myocardial ECV (bolus or infusion technique) and pre-contrast T1 are biomarkers for cardiac AL amyloid and they predict mortality in systemic amyloidosis.
Keywords: Amyloid; CMR; Cardiomyopathy; ECV; Heart failure; T1 mapping.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
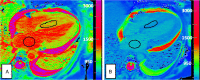


Comment in
-
T1 mapping and amyloid cardiomyopathy: how much better can it get?Eur Heart J. 2015 Jan 21;36(4):203-5. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu442. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Eur Heart J. 2015. PMID: 25411192 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA, Kyle RA, Lacy MQ, Burritt MF, Therneau TM, Greipp PR, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Rajkumar SV, Fonseca R, Zeldenrust SR, McGregor CG, Jaffe AS. Serum cardiac troponins and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide: a staging system for primary systemic amyloidosis. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:3751–3757. - PubMed
-
- Dubrey SW, Cha K, Anderson J, Chamarthi B, Reisinger J, Skinner M, Falk RH. The clinical features of immunoglobulin light-chain (AL) amyloidosis with heart involvement. QJM. 1998;91:141–157. - PubMed
-
- Perlini S, Salinaro F, Cappelli F, Perfetto F, Bergesio F, Alogna A, Mussinelli R, Boldrini M, Raimondi A, Musca F, Palladini G, Merlini G. Prognostic value of fragmented QRS in cardiac AL amyloidosis. Int J Cardiol. 2013;167:2156–2161. - PubMed
-
- Miller F, Jr, Bellavia D. Comparison of right ventricular longitudinal strain imaging, tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion, and cardiac biomarkers for early diagnosis of cardiac involvement and risk stratification in primary systematic (AL) amyloidosis: a 5-year cohort study: reply. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013;14:91–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

