Piecewise linear and Boolean models of chemical reaction networks
- PMID: 25412739
- PMCID: PMC4258194
- DOI: 10.1007/s11538-014-0040-x
Piecewise linear and Boolean models of chemical reaction networks
Abstract
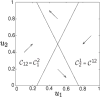
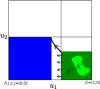
Models of biochemical networks are frequently complex and high-dimensional. Reduction methods that preserve important dynamical properties are therefore essential for their study. Interactions in biochemical networks are frequently modeled using Hill functions ([Formula: see text]). Reduced ODEs and Boolean approximations of such model networks have been studied extensively when the exponent [Formula: see text] is large. However, while the case of small constant [Formula: see text] appears in practice, it is not well understood. We provide a mathematical analysis of this limit and show that a reduction to a set of piecewise linear ODEs and Boolean networks can be mathematically justified. The piecewise linear systems have closed-form solutions that closely track those of the fully nonlinear model. The simpler, Boolean network can be used to study the qualitative behavior of the original system. We justify the reduction using geometric singular perturbation theory and compact convergence, and illustrate the results in network models of a toggle switch and an oscillator.
Figures











References
-
- Abou-Jaoudé W, Ouattara D, Kaufman M. From structure to dynamics: frequency tuning in the p53-mdm2 network: I. logical approach. J Theor Biol. 2009;258(4):561–577. - PubMed
-
- Abou-Jaoudé W, Ouattara D, Kaufman M. From structure to dynamics: fre quency tuning in the p53-mdm2 network: II. differential and stochastic approaches. J Theor Biol. 2010;264(4):1177–1189. - PubMed
-
- Aguda D. Modeling the Cell Division Cycle, Lecture Notes in Mathematics. Vol. 1872. Springer; 2006. pp. 1–22.
-
- Alon U. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits. Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

