Characteristics of long non-coding RNAs in the Brown Norway rat and alterations in the Dahl salt-sensitive rat
- PMID: 25413633
- PMCID: PMC4894415
- DOI: 10.1038/srep07146
Characteristics of long non-coding RNAs in the Brown Norway rat and alterations in the Dahl salt-sensitive rat
Abstract
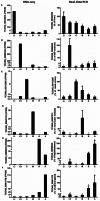
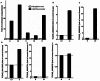
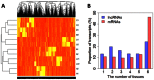
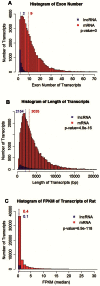
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are potentially important mediators of genomic regulation. lncRNAs, however, remain poorly characterized in the rat model organism widely used in biomedical research. Using poly(A)-independent and strand-specific RNA-seq, we identified 1,500 to 1,800 lncRNAs expressed in each of the following tissues of Brown Norway rats: the renal cortex, renal outer medulla, liver, cardiac left ventricle, adrenal gland, and hypothalamus. Expression and the binding of histone H3K4me3 to promoter regions were confirmed for several lncRNAs. Rat lncRNA expression appeared to be more tissue-specific than mRNA. Rat lncRNAs had 4.5 times fewer exons and 29% shorter transcripts than mRNA. The median cumulative abundance of rat lncRNAs was 53% of that of mRNA. Approximately 28% of the lncRNAs identified in the renal outer medulla appeared to lack a poly(A) tail. Differential expression of 74 lncRNAs was detected in the renal outer medulla between Dahl SS rats, a model of salt-sensitive hypertension, and salt-insensitive, congenic SS.13(BN26) rats fed a high-salt diet. Two of the differentially expressed lncRNAs, which were confirmed, were located within the congenic region and contained several sequence variants. The study identified genome-wide characteristics of lncRNAs in the rat model and suggested a role of lncRNAs in hypertension.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

