Glycerophosphate/Acylglycerophosphate acyltransferases
- PMID: 25415055
- PMCID: PMC4280512
- DOI: 10.3390/biology3040801
Glycerophosphate/Acylglycerophosphate acyltransferases
Abstract
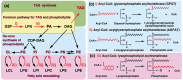
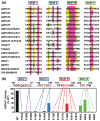
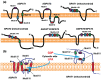
Acyl-CoA:glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (GPAT) and acyl-CoA: 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (AGPAT) are involved in the de novo synthesis of triacylglycerol (TAG) and glycerophospholipids. Many enzymes belonging to the GPAT/AGPAT family have recently been identified and their physiological or pathophysiological roles have been proposed. The roles of GPAT/AGPAT in the synthesis of TAG and obesity-related diseases were revealed through the identification of causative genes of these diseases or analyses of genetically manipulated animals. Recent studies have suggested that some isoforms of GPAT/AGPAT family enzymes are involved in the fatty acid remodeling of phospholipids. The enzymology of GPAT/AGPAT and their physiological/ pathological roles in the metabolism of glycerolipids have been described and discussed in this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase enzyme (LPAAT4) with a possible role for incorporating docosahexaenoic acid into brain glycerophospholipids.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 10;443(2):718-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.043. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24333445
-
Transcriptional Regulation of Acyl-CoA:Glycerol-sn-3-Phosphate Acyltransferases.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 22;20(4):964. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040964. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30813330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemistry, physiology, and genetics of GPAT, AGPAT, and lipin enzymes in triglyceride synthesis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Jun;296(6):E1195-209. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90958.2008. Epub 2009 Mar 31. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19336658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular identification of microsomal acyl-CoA:glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, a key enzyme in de novo triacylglycerol synthesis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 26;103(52):19695-700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0609140103. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17170135 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of the human 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate-O-acyltransferase isoform 10/glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase isoform 3.J Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;42(6):469-78. doi: 10.1677/JME-09-0010. Epub 2009 Mar 24. J Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19318427 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Non-Coding and Regulatory RNAs as Epigenetic Remodelers of Fatty Acid Homeostasis in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 9;12(10):2890. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102890. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIIODOTHYRONINE ACTIVATES GLYCEROL-3-PHOSPHATE ACYLTRANSFERASE 3 VIA AGGTCA-LIKE-DIRECT-REPEAT-4 TYPE THYROID HORMONE RESPONSE ELEMENT.Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2020 Apr-Jun;16(2):129-135. doi: 10.4183/aeb.2020.129. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar). 2020. PMID: 33029227 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Interactions Between Flaviviruses and Mosquito Vectors.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 5;12:763195. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.763195. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34899388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular identification of transmembrane protein 68 as an endoplasmic reticulum-anchored and brain-specific protein.PLoS One. 2017 May 4;12(5):e0176980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176980. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28472192 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-specific deletion of Agpat5 protects against liquid sucrose-induced hyperinsulinemia and glucose intolerance.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024 Dec 31;741:151059. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2024.151059. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39608054 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

