Latent factor modeling of four schizotypy dimensions with theory of mind and empathy
- PMID: 25415195
- PMCID: PMC4240595
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113853
Latent factor modeling of four schizotypy dimensions with theory of mind and empathy
Abstract
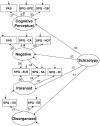
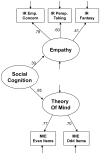
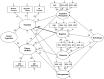
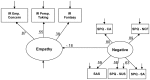
Preliminary evidence suggests that theory of mind and empathy relate differentially to factors of schizotypy. The current study assessed 686 undergraduate students and used structural equation modeling to examine links between a four-factor model of schizotypy with performance on measures of theory of mind (Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test [MIE]) and empathy (Interpersonal Reactivity Index [IRI]). Schizotypy was assessed using three self-report measures which were simultaneously entered into the model. Results revealed that the Negative factor of schizotypy showed a negative relationship with the Empathy factor, which was primarily driven by the Empathic Concern subscale of the IRI and the No Close Friends and Constricted Affect subscales of the Schizotypal Personality Questionnaire. These findings are consistent with a growing body of literature suggesting a relatively specific relationship between negative schizotypy and empathy, and are consistent with several previous studies that found no relationship between MIE performance and schizotypy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Esterberg ML, Compton MT. The psychosis continuum and categorical versus dimensional diagnostic approaches. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2009;11(3):179–184. - PubMed
-
- Fogelson DL, Nuechterlein KH, Asarnow RA, Payne DL, Subotnik KL, et al. Avoidant personality disorder is a separable schizophrenia-spectrum personality disorder even when controlling for the presence of paranoid and schizotypal personality disorders The UCLA family study. Schizophr Res. 2007;91(1–3):192–199. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calkins ME, Curtis CE, Grove WM, Iacono WG. Multiple dimensions of schizotypy in first degree biological relatives of schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Bull. 2004;30(2):317–325. - PubMed
-
- Kendler KS, McGuire M, Gruenberg AM, Walsh D. Schizotypal symptoms and signs in the Roscommon Family Study. Their factor structure and familial relationship with psychotic and affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;52(4):296–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

