JAK inhibition and progressive kidney disease
- PMID: 25415616
- PMCID: PMC4673981
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000079
JAK inhibition and progressive kidney disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: To review the role of Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling in the progression of chronic kidney diseases.
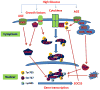
Recent findings: The JAK-STAT pathway transmits signals from extracellular ligands, including many cytokines and chemokines. While these responses are best characterized in lymphoid cells, they also occur in kidney cells such as podocytes, mesangial cells, and tubular cells. JAK-STAT expression and signaling abnormalities occur in humans and animal models of different chronic kidney diseases. Enhanced expression and augmented activity of JAK1, JAK2, and STAT3 promote diabetic nephropathy and their inhibition appears to reduce the disease. Activation of JAK-STAT signaling in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease may play an important role in cyst growth. Activation of JAK-STAT signaling promotes HIV-associated nephropathy and may also participate in the tubular responses to chronic obstructive uropathy. On the basis of data from experimental models, inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling, via increased expression of the suppressors of cytokine signaling proteins or pharmacologic inhibition of JAK and STAT proteins, could play a therapeutic role in multiple chronic kidney diseases.
Summary: Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway appears to play a role in the progression of some chronic kidney diseases. More work is needed to determine the specific role the pathway plays in individual diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Li J, Gobe G. Protein kinase C activation and its role in kidney disease. Nephrology (Carlton) 2006 Oct;11(5):428–34. eng. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Chen JK, Harris RC. Angiotensin II induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal epithelial cells through reactive oxygen species/Src/caveolin-mediated activation of an epidermal growth factor receptor-extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Mar;32(5):981–91. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lan HY, Chung AC. TGF-beta/Smad signaling in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2012 May;32(3):236–43. - PubMed
-
- Wada J, Makino H. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond) 2013 Feb;124(3):139–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

