Null mutation of 5α-reductase type I gene alters ethanol consumption patterns in a sex-dependent manner
- PMID: 25416204
- PMCID: PMC4425631
- DOI: 10.1007/s10519-014-9694-2
Null mutation of 5α-reductase type I gene alters ethanol consumption patterns in a sex-dependent manner
Abstract
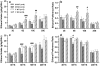
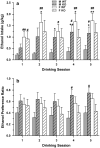
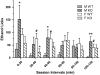
The neuroactive steroid allopregnanolone (ALLO) is a positive modulator of GABAA receptors, and manipulation of neuroactive steroid levels via injection of ALLO or the 5α-reductase inhibitor finasteride alters ethanol self-administration patterns in male, but not female, mice. The Srd5a1 gene encodes the enzyme 5α-reductase-1, which is required for the synthesis of ALLO. The current studies investigated the influence of Srd5a1 deletion on voluntary ethanol consumption in male and female wildtype (WT) and knockout (KO) mice. Under a continuous access condition, 6 and 10 % ethanol intake was significantly greater in KO versus WT females, but significantly lower in KO versus WT males. In 2-h limited access sessions, Srd5a1 deletion retarded acquisition of 10 % ethanol intake in female mice, but facilitated it in males, versus respective WT mice. The present findings demonstrate that the Srd5a1 gene modulates ethanol consumption in a sex-dependent manner that is also contingent upon ethanol access condition and concentration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

