MEF2 transcription factors regulate distinct gene programs in mammalian skeletal muscle differentiation
- PMID: 25416778
- PMCID: PMC4294490
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.589838
MEF2 transcription factors regulate distinct gene programs in mammalian skeletal muscle differentiation
Abstract
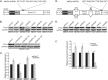
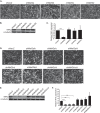
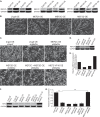
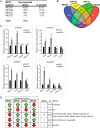
Skeletal muscle differentiation requires precisely coordinated transcriptional regulation of diverse gene programs that ultimately give rise to the specialized properties of this cell type. In Drosophila, this process is controlled, in part, by MEF2, the sole member of an evolutionarily conserved transcription factor family. By contrast, vertebrate MEF2 is encoded by four distinct genes, Mef2a, -b, -c, and -d, making it far more challenging to link this transcription factor to the regulation of specific muscle gene programs. Here, we have taken the first step in molecularly dissecting vertebrate MEF2 transcriptional function in skeletal muscle differentiation by depleting individual MEF2 proteins in myoblasts. Whereas MEF2A is absolutely required for proper myoblast differentiation, MEF2B, -C, and -D were found to be dispensable for this process. Furthermore, despite the extensive redundancy, we show that mammalian MEF2 proteins regulate a significant subset of nonoverlapping gene programs. These results suggest that individual MEF2 family members are able to recognize specific targets among the entire cohort of MEF2-regulated genes in the muscle genome. These findings provide opportunities to modulate the activity of MEF2 isoforms and their respective gene programs in skeletal muscle homeostasis and disease.
Keywords: Differentiation; Myogenesis; RNA Interference (RNAi); Transcription Factor; Transcriptomics.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Buckingham M., Rigby P. W. (2014) Gene regulatory networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis. Dev. Cell 28, 225–238 - PubMed
-
- Braun T., Gautel M. (2011) Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle differentiation, growth and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 349–361 - PubMed
-
- Black B. L., Olson E. N. (1998) Transcriptional control of muscle development by myocyte enhancer factor-2 (MEF2) proteins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14, 167–196 - PubMed
-
- Potthoff M. J., Olson E. N. (2007) MEF2: a central regulator of diverse developmental programs. Development. 134, 4131–4140 - PubMed
-
- Sandmann T., Jensen L. J., Jakobsen J. S., Karzynski M. M., Eichenlaub M. P., Bork P., Furlong E. E. (2006) A temporal map of transcription factor activity: Mef2 directly regulates target genes at all stages of muscle development. Dev. Cell 10, 797–807 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

