Conflicts of interest and critiques of the use of systematic reviews in policymaking: an analysis of opinion articles
- PMID: 25417178
- PMCID: PMC4241194
- DOI: 10.1186/2046-4053-3-122
Conflicts of interest and critiques of the use of systematic reviews in policymaking: an analysis of opinion articles
Abstract
Background: Strong opinions for or against the use of systematic reviews to inform policymaking have been published in the medical literature. The purpose of this paper was to examine whether funding sources and author financial conflicts of interest were associated with whether an opinion article was supportive or critical of the use of systematic reviews for policymaking. We examined the nature of the arguments within each article, the types of disclosures present, and whether these articles are being cited in the academic literature.
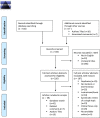
Methods: We searched for articles that expressed opinions about the use of systematic reviews for policymaking. We included articles that presented opinions about the use of systematic reviews for policymaking and categorized each article as supportive or critical of such use. We extracted all arguments regarding the use of systematic reviews from each article and inductively coded each as internal or external validity argument, categorized disclosed funding sources, conflicts of interest, and article types, and systematically searched for undisclosed financial ties. We counted the number of times each article has been cited in the "Web of Science." We report descriptive statistics.
Results: Articles that were critical of the use of systematic reviews (n=25) for policymaking had disclosed or undisclosed industry ties 2.3 times more often than articles that were supportive of the use (n=34). We found that editorials, comments, letters, and perspectives lacked published disclosures nearly twice as often (60% v. 33%) as other types of articles. We also found that editorials, comments, letters, and perspectives were less frequently cited in the academic literature than other article types (median number of citations=5 v. 19).
Conclusions: It is important to consider whether an article has industry ties when evaluating the strength of the argument for or against the use of systematic reviews for policymaking. We found that journal conflict of interest disclosures are often inadequate, particularly for editorials, comments, letters, and perspectives and that these articles are being cited as evidence in the academic literature. Our results further suggest the need for more consistent and complete disclosure for all article types.
Similar articles
-
Funding source and conflict of interest disclosures by authors and editors in gastroenterology specialty journals revisited.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012 Mar;35(6):690-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04989.x. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012. PMID: 22257079
-
Reporting of conflicts of interest in meta-analyses of trials of pharmacological treatments.JAMA. 2011 Mar 9;305(10):1008-17. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.257. JAMA. 2011. PMID: 21386079 Review.
-
Funding source and conflict of interest disclosures by authors and editors in gastroenterology specialty journals.Am J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jun;102(6):1146-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01268.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17531007
-
Changing conclusions on secondhand smoke in a sudden infant death syndrome review funded by the tobacco industry.Pediatrics. 2005 Mar;115(3):e356-66. doi: 10.1542/peds.2004-1922. Pediatrics. 2005. PMID: 15741361
-
Guideline funding and conflicts of interest: article 4 in Integrating and coordinating efforts in COPD guideline development. An official ATS/ERS workshop report.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012 Dec;9(5):234-42. doi: 10.1513/pats.201208-057ST. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2012. PMID: 23256165 Review.
Cited by
-
WHO/ILO work-related burden of disease and injury: Protocol for systematic reviews of exposure to occupational ergonomic risk factors and of the effect of exposure to occupational ergonomic risk factors on osteoarthritis of hip or knee and selected other musculoskeletal diseases.Environ Int. 2019 Apr;125:554-566. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.09.053. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Environ Int. 2019. PMID: 30583853 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of occupational exposure to welding fumes on trachea, bronchus and lung cancer: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury.Environ Int. 2020 Dec;145:106089. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106089. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 32950789 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of exposure to long working hours on alcohol consumption, risky drinking and alcohol use disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury.Environ Int. 2021 Jan;146:106205. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106205. Epub 2020 Nov 12. Environ Int. 2021. PMID: 33189992 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Nonnutritive Sweeteners on the BMI of Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Prospective Cohort Studies.Adv Nutr. 2024 Dec;15(12):100292. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2024.100292. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Adv Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39299839 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of exposure to long working hours on ischaemic heart disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury.Environ Int. 2020 Sep;142:105739. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.105739. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Environ Int. 2020. PMID: 32505014 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sweet M, Moynihan R, Fund MM. Improving Population Health: The Uses of Systematic Reviews. New York: Milbank Memorial Fund; 2007.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources