FMR1 epigenetic silencing commonly occurs in undifferentiated fragile X-affected embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 25418717
- PMCID: PMC4235235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2014.09.001
FMR1 epigenetic silencing commonly occurs in undifferentiated fragile X-affected embryonic stem cells
Abstract
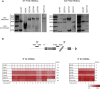
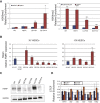
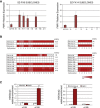
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is the most common heritable form of cognitive impairment. It results from epigenetic silencing of the X-linked FMR1 gene by a CGG expansion in its 5'-untranslated region. Taking advantage of a large set of FXS-affected human embryonic stem cell (HESC) lines and isogenic subclones derived from them, we show that FMR1 hypermethylation commonly occurs in the undifferentiated state (six of nine lines, ranging from 24% to 65%). In addition, we demonstrate that hypermethylation is tightly linked with FMR1 transcriptional inactivation in undifferentiated cells, coincides with loss of H3K4me2 and gain of H3K9me3, and is unrelated to CTCF binding. Taken together, these results demonstrate that FMR1 epigenetic gene silencing takes place in FXS HESCs and clearly highlights the importance of examining multiple cell lines when investigating FXS and most likely other epigenetically regulated diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Castellví-Bel S., Milà M., Soler A., Carrió A., Sánchez A., Villa M., Jiménez M.D., Estivill X. Prenatal diagnosis of fragile X syndrome: (CGG)n expansion and methylation of chorionic villus samples. Prenat. Diagn. 1995;15:801–807. - PubMed
-
- Coffee B., Zhang F., Warren S.T., Reines D. Acetylated histones are associated with FMR1 in normal but not fragile X-syndrome cells. Nat. Genet. 1999;22:98–101. - PubMed
-
- Devys D., Biancalana V., Rousseau F., Boué J., Mandel J.L., Oberlé I. Analysis of full fragile X mutations in fetal tissues and monozygotic twins indicate that abnormal methylation and somatic heterogeneity are established early in development. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1992;43:208–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

