Validation of MicroAeth® as a Black Carbon Monitor for Fixed-Site Measurement and Optimization for Personal Exposure Characterization
- PMID: 25419215
- PMCID: PMC4240508
- DOI: 10.4209/aaqr.2013.03.0088
Validation of MicroAeth® as a Black Carbon Monitor for Fixed-Site Measurement and Optimization for Personal Exposure Characterization
Abstract
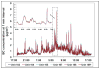
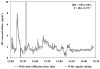
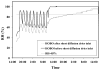
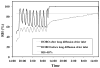
This paper reports on validation experiments with the recently developed microAeth®, a pocket-sized device which is able to obtain real-time and personal measurements of black carbon (BC) aerosol. High reproducibility was observed when comparing the results from six new individual units during fixed-site monitoring out of a window (relative standard deviation [RSD] = 8% ± 5%, N = 1442). The results obtained from the microAeth devices agreed with those obtained from a full size rack mounted Aethalometer, based on both the 1-minute data (R = 0.92, slope = 1.01 ± 0.01, N = 1380) and 24-h average data. The 24-h average of real time data obtained from the microAeths was comparable to the BC concentration obtained from 24-h integrated PM2.5 filter deposits, as determined by multi-wavelength optical absorption (R = 0.98, slope = 0.92 ± 0.07, N = 12). Rapid environmental changes in relative humidity (RH) and temperature (T) can result in false positive and negative peaks in the real time BC concentrations, though averages > 1-2-hour are only minimally affected. An inlet with a diffusion drier based on Nafion® tubing was developed in order to use BC data with a high time resolution. The data shows that the diffusion drier greatly reduce the impacts from rapid changes in RH and T when the monitoring system is worn in close proximity to the body (e.g., in the vest pocket).
Keywords: Black carbon; Fixed-site monitoring; Humidity; MicroAeth; Personal exposure.
Figures



References
-
- Akhter MS, Chughtai AR, Smith DM. The Structure of Hexane Soot II: Extraction Studies. Appl Spectrosc. 1985;39:154–167.
-
- Allen GA, Lawrence J, Koutrakis P. Field Validation of a Semi-continuous Method for Aerosol Black Carbon (Aethalometer) and Temporal Patterns of Summertime Hourly Black Carbon Measurements in Southwestern PA. Atmos Environ. 1999;33:817–823.
-
- Andreae MO. The Dark Side of Aerosols. Nature. 2001;409:671–672. - PubMed
-
- Arnott WP, Moosmuller H, Sheridan PJ, Ogren JA, Raspet R, Slaton WV, Hand JL, Kreidenweis SM, Collett JL. Photoacoustic and Filter-based Ambient Aerosol Light Absorption Measurements: Instrument Comparisons and the Role of Relative Humidity. J Geophys Res. 2003;108:AAC 15-1–AAC 15-11.
-
- Babich P, Davey M, Allen G, Koutrakis P. Method Comparisons for Particulate Nitrate, Elemental Carbon, and PM2.5 Mass in Seven US Cities. J Air Waste Manage Assoc. 2000;50:1095–1105. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
