Elevated expression of AKR1C3 increases resistance of cancer cells to ionizing radiation via modulation of oxidative stress
- PMID: 25419901
- PMCID: PMC4242615
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111911
Elevated expression of AKR1C3 increases resistance of cancer cells to ionizing radiation via modulation of oxidative stress
Abstract
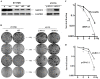
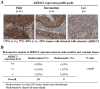
With the aim to elucidate the etiology of radioresistance, we explored the genetic alterations in non-radioresistant vs. resistant esophageal cancer cells acquired by long-term fractionated radiation. We found AKR1C3, an aldo-keto reductase expressed seldom in most human tissues, expressed higher in radioresistance-acquired cells. Suppression of AKR1C3 via RNAi or its chemical inhibitors restored the sensitivity of the acquired tumor cells and xenograft BALB/c nude mice to ionizing radiation (IR). Cellular monitoring of the oxidative stress in the AKR1C3-elevated cells indicated that IR-induced ROS accumulation and the concomitant DNA damage was significantly alleviated, and such protective consequence disappeared upon AKR1C3 knockdown. These findings uncover the potential involvement of AKR1C3 in removal of cellular ROS and explain, at least partially, the acquired radioresistance by AKR1C3 overexpression. A retrospective analysis of esophageal carcinomas also indicated a significant expression of AKR1C3 in radio-resistant but not radio-sensitive surgical samples. Our study may provide a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis of radiotherapy and even direct a targeted therapy for esophageal cancer and other tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Bernier J, Hall EJ, Giaccia A (2004) Radiation oncology: a century of achievements. Nat Rev Cancer 4: 737–747. - PubMed
-
- Riley PA (1994) Free radicals in biology: oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 65: 27–33. - PubMed
-
- Majima HJ, Indo HP, Tomita K, Suenaga S, Motoori S, et al.. (2006). Intracellular oxidative stress caused by ionizing radiation. In: Singh KK (ed.) Oxidative Stress, Disease and Cancer. London: Imperial College Press. pp.61–83.
-
- Spitz DR, Azzam EI, Li JJ, Gius D (2004) Metabolic oxidation/reduction reactions and cellular responses to ionizing radiation: A unifying concept in stress response biology. Cancer And Metastasis Reviews 23: 311–322. - PubMed
-
- Roos WP, Kaina B (2006) DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends In Molecular Medicine 12: 440–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

