Exploring inequities in skilled care at birth among migrant population in a metropolitan city Addis Ababa, Ethiopia; a qualitative study
- PMID: 25421142
- PMCID: PMC4246478
- DOI: 10.1186/s12939-014-0110-6
Exploring inequities in skilled care at birth among migrant population in a metropolitan city Addis Ababa, Ethiopia; a qualitative study
Abstract
Introduction: Ethiopia records high levels of inequity in skilled birth care (SBC), where the gaps are much wider among urban migrant women. An intervention project has been conducted in Addis Ababa, intending to improve quality and to ensure equitable access to maternal and newborn care services. As part of the project, this study explored the inequities in maternal health care among migrant women in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
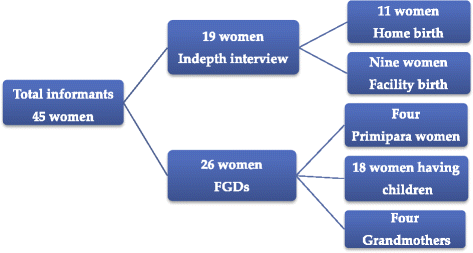
Methods: A qualitative community based study was conducted from April to May 2014 among 45 purposefully selected internal migrant women. Eleven women who give birth at home and eight who gave birth at health facility in the last year preceding the study participated in in-depth interviews. Four primiparas' young women, 18 women who have children and four grandmothers participated in focus group discussions. Guides were used for data collection. Using framework and content analysis three themes and four sub-themes emerged.
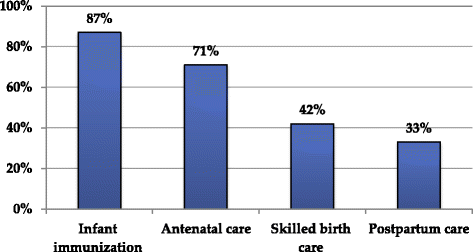
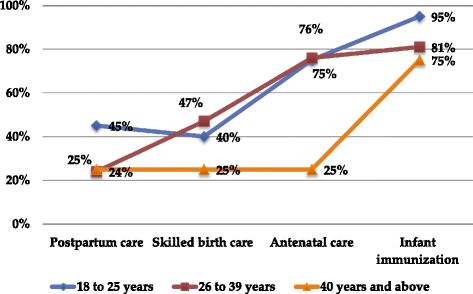
Results: According to the informants, patterns of service utilization varied widely. Antenatal care and infant immunization were fairly equally accessed across the different age groups of informants in their most recent birth irrespective of where they gave birth, yet obvious access gaps were reported in SBC and postpartum care. There were missed opportunities to postpartum care. Only few women had received postpartum care despite, some of the women delivering in the health facility and many visiting the health facilities for infant immunization. The four emerged sub-themes reportedly influencing access and utilization of SBC were social influences, physical access to health facility, risk perceptions and perceived quality of care and disrespect. Of these social, structural and health system factors, informants presented experiences of disrespectful care as a powerful deterrent to SBC.
Conclusions: Migrant women constitute disadvantaged communities in Addis Ababa and have unequal access to SBC and postpartum care. This happens in the backdrop of fairly equitable access to antenatal care, infant immunization, universal health coverage and free access to maternal and newborn care. Addressing the underlying determinants for the inequities and bridging the quality gaps in maternal and newborn services with due emphasis on respectful care for migrant women need tailored intervention and prioritization.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Women's perspectives on the measures that need to be taken to increase the use of health-care facility delivery service among slums women, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: a qualitative study.Reprod Health. 2021 Aug 23;18(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01221-9. Reprod Health. 2021. PMID: 34425837 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal health care access among migrant women labourers in the selected brick kilns of district Faridabad, Haryana: mixed method study on equity and access.Int J Equity Health. 2018 Nov 20;17(1):171. doi: 10.1186/s12939-018-0886-x. Int J Equity Health. 2018. PMID: 30458803 Free PMC article.
-
Skilled delivery care service utilization in Ethiopia: analysis of rural-urban differentials based on national demographic and health survey (DHS) data.Afr Health Sci. 2014 Dec;14(4):974-84. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v14i4.29. Afr Health Sci. 2014. PMID: 25834510 Free PMC article.
-
Inequities in utilization of reproductive and maternal health services in Ethiopia.Int J Equity Health. 2017 Jun 19;16(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s12939-017-0602-2. Int J Equity Health. 2017. PMID: 28629358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migrant women's experiences of pregnancy, childbirth and maternity care in European countries: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 11;15(2):e0228378. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228378. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32045416 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Developing and evaluating human-centered design solutions for enhancing maternal health service utilization among vulnerable pregnant women in Oromia, Ethiopia: Study protocol for a quasi-experimental study.Gates Open Res. 2025 Feb 21;8:93. doi: 10.12688/gatesopenres.16277.3. eCollection 2024. Gates Open Res. 2025. PMID: 39801791 Free PMC article.
-
Health service behaviors of migrants: A conceptual framework.Front Public Health. 2023 Apr 14;11:1043135. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1043135. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37124818 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating the mistreatment of childbearing women: evaluation of respectful maternity care intervention in Ethiopian hospitals.BMJ Open. 2020 Sep 3;10(9):e038871. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038871. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32883738 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of disrespectful maternity care on childbirth complications: a multicentre cross-sectional study in Ethiopia.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024 May 21;24(1):380. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06574-0. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2024. PMID: 38773395 Free PMC article.
-
The Mistreatment of Women during Childbirth in Health Facilities Globally: A Mixed-Methods Systematic Review.PLoS Med. 2015 Jun 30;12(6):e1001847; discussion e1001847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001847. eCollection 2015 Jun. PLoS Med. 2015. PMID: 26126110 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lee AC, Cousens S, Darmstadt GL, Blencowe H, Pattinson R, Moran NF, Hofmeyr GJ, Haws RA, Bhutta SZ, Lawn JE. Care during labor and birth for the prevention of intrapartum-related neonatal deaths: a systematic review and Delphi estimation of mortality effect. BMC Public Health. 2011;11 Suppl 3:S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-S3-S10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhutta ZA, Chopra M, Axelson H, Berman P, Boerma T, Bryce J, Bustreo F, Cavagnero E, Cometto G, de Daelmans B, Francisco A, Fogstad H, Gupta N, Laski L, Lawn J, Maliqi B, Mason E, Pitt C, Requejo J, Starrs A, Victora CG, Wardlaw T. Countdown to 2015 decade report (2000–10): taking stock of maternal, newborn, and child survival. Lancet. 2010;375(9730):2032–2044. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60678-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

