Therapeutic activity of glycoengineered anti-GM2 antibodies against malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 25421609
- PMCID: PMC4317781
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12575
Therapeutic activity of glycoengineered anti-GM2 antibodies against malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
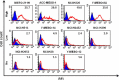
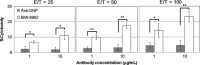
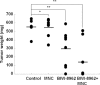
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a rare and highly aggressive neoplasm that arises from the pleural, pericardial, or peritoneal lining. Although surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and combinations of these therapies are used to treat MPM, the median survival of such patients is dismal. Therefore, there is a compelling need to develop novel therapeutics with different modes of action. Ganglioside GM2 is a glycolipid that has been shown to be overexpressed in various types of cancer. However, there are no published reports regarding the use of GM2 as a potential therapeutic target in cases of MPM. In this study, we evaluated the efficacy of the anti-GM2 antibody BIW-8962 as an anti-MPM therapeutic using in vitro and in vivo assays. Consequently, the GM2 expression in the MPM cell lines was confirmed using flow cytometry. In addition, eight of 11 cell lines were GM2-positive (73%), although the GM2 expression was variable. BIW-8962 showed a significant antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity activity against the GM2-expressing MPM cell line MSTO-211H, the effect of which depended on the antibody concentration and effector/target ratio. In an in vivo orthotropic mouse model using MSTO-211H cells, BIW-8962 significantly decreased the incidence and size of tumors. Additionally, the GM2 expression was confirmed in the MPM clinical specimens. Fifty-eight percent of the MPM tumors were positive for GM2, with individual variation in the intensity and frequency of staining. These data suggest that anti-GM2 antibodies may become a therapeutic option for MPM patients.
Keywords: Antibodies; antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity; ganglioside GM2; mesothelioma; therapeutics.
© 2014 The Authors. Cancer Science published by Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1198-205. doi: 10.1111/cas.12985. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27294401 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic antitumor efficacy of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody, cetuximab, against malignant pleural mesothelioma.Int J Oncol. 2012 Nov;41(5):1610-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1607. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22922885 Free PMC article.
-
Aminopeptidase N/CD13 as a potential therapeutic target in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Eur Respir J. 2018 May 24;51(5):1701610. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01610-2017. Print 2018 May. Eur Respir J. 2018. PMID: 29519924
-
[Systemic Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017 Dec;44(13):2041-2047. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017. PMID: 29361614 Review. Japanese.
-
Antiangiogenic therapies for malignant pleural mesothelioma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011 Jan 1;16(2):740-8. doi: 10.2741/3716. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2011. PMID: 21196199 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effects of anti-GM2 CAR-T cells expressing IL-7 and CCL19 for GM2-positive solid cancer in xenograft model.Cancer Med. 2023 Jun;12(11):12569-12580. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5907. Epub 2023 Apr 9. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37031457 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor activity of alectinib in tumor cells with NCOA4-RET.Oncotarget. 2017 May 16;8(43):73766-73773. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17900. eCollection 2017 Sep 26. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29088743 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor effect of novel anti-podoplanin antibody NZ-12 against malignant pleural mesothelioma in an orthotopic xenograft model.Cancer Sci. 2016 Sep;107(9):1198-205. doi: 10.1111/cas.12985. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27294401 Free PMC article.
-
Podoplanin promotes progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma by regulating motility and focus formation.Cancer Sci. 2017 Apr;108(4):696-703. doi: 10.1111/cas.13190. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Cancer Sci. 2017. PMID: 28182302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Connelly RR, Spirtas R, Myers MH, Percy CL, Fraumeni JF., Jr Demographic patterns for mesothelioma in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1987;78:1053–60. - PubMed
-
- Ismail-Khan R, Robinson LA, Williams CC, Jr, Garrett CR, Bepler G, Simon GR. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: a comprehensive review. Cancer Control. 2006;13:255–63. - PubMed
-
- Ruffie P, Feld R, Minkin S, et al. Diffuse malignant mesothelioma of the pleura in Ontario and Quebec: a retrospective study of 332 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1989;7:1157–68. - PubMed
-
- Pass HI, Kranda K, Temeck BK, Feuerstein I, Steinberg SM. Surgically debulked malignant pleural mesothelioma: results and prognostic factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 1997;4:215–22. - PubMed
-
- Rusch VW, Piantadosi S, Holmes EC. The role of extrapleural pneumonectomy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. A Lung Cancer Study Group trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991;102:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

