Role of Type 1 Diabetes-Associated SNPs on Risk of Autoantibody Positivity in the TEDDY Study
- PMID: 25422107
- PMCID: PMC4407865
- DOI: 10.2337/db14-1497
Role of Type 1 Diabetes-Associated SNPs on Risk of Autoantibody Positivity in the TEDDY Study
Abstract
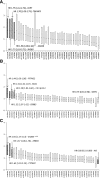
The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study prospectively follows 8,677 children enrolled from birth who carry HLA-susceptibility genotypes for development of islet autoantibodies (IA) and type 1 diabetes (T1D). During the median follow-up time of 57 months, 350 children developed at least one persistent IA (GAD antibody, IA-2A, or micro insulin autoantibodies) and 84 of them progressed to T1D. We genotyped 5,164 Caucasian children for 41 non-HLA single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that achieved genome-wide significance for association with T1D in the genome-wide association scan meta-analysis conducted by the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. In TEDDY participants carrying high-risk HLA genotypes, eight SNPs achieved significant association to development of IA using time-to-event analysis (P < 0.05), whereof four were significant after adjustment for multiple testing (P < 0.0012): rs2476601 in PTPN22 (hazard ratio [HR] 1.54 [95% CI 1.27-1.88]), rs2292239 in ERBB3 (HR 1.33 [95% CI 1.14-1.55]), rs3184504 in SH2B3 (HR 1.38 [95% CI 1.19-1.61]), and rs1004446 in INS (HR 0.77 [0.66-0.90]). These SNPs were also significantly associated with T1D in particular: rs2476601 (HR 2.42 [95% CI 1.70-3.44]). Although genes in the HLA region remain the most important genetic risk factors for T1D, other non-HLA genetic factors contribute to IA, a first step in the pathogenesis of T1D, and the progression of the disease.
© 2015 by the American Diabetes Association. Readers may use this article as long as the work is properly cited, the use is educational and not for profit, and the work is not altered.
Figures
References
-
- Lambert AP, Gillespie KM, Thomson G, et al. . Absolute risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes defined by human leukocyte antigen class II genotype: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004;89:4037–4043 - PubMed
-
- Kaprio J, Tuomilehto J, Koskenvuo M, et al. . Concordance for type 1 (insulin-dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in a population-based cohort of twins in Finland. Diabetologia 1992;35:1060–1067 - PubMed
-
- Redondo MJ, Jeffrey J, Fain PR, Eisenbarth GS, Orban T. Concordance for islet autoimmunity among monozygotic twins. N Engl J Med 2008;359:2849–2850 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK95300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001427/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD050196/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD037800/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK63863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK63861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK069878/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

