The mystery of recurrent idiopathic cerebrovascular and coronary arterial thrombosis
- PMID: 25422328
- PMCID: PMC4244328
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205430
The mystery of recurrent idiopathic cerebrovascular and coronary arterial thrombosis
Abstract
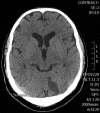
A 46-year-old man presented to our hospital with ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Previous records revealed a history of recurrent non-STEMI, stroke and transient ischaemic attacks. He was thoroughly investigated with coronary angiography, a cerebral CT angiography, thrombophilia panel and autoimmune screening tests, all of which proved negative. His current episode of STEMI resulted while on dual antiplatelet therapy; the patient was investigated for P2Y12 receptor resistance, which was also negative. A diagnosis of idiopathic recurrent arterial thrombosis was established and the patient was discharged home on aspirin and warfarin. Routine follow-up has revealed no recurrence of symptoms.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World heath statistics. Promoting Cardiovascular Health in the Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. Chapter 2 p 49. Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Preventing the Global Epidemic of Cardiovascular Disease: Meeting the Challenges in Developing Countries; Fuster V, Kelly BB, editors. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2010 Geneva: World Health Organization, 2009.
-
- Chatterjee K. Cardiology an illustrated textbook. Vol 1 Jaypee Brothers Medical publishers. 2012:829.
-
- Shah R, Duncan SJ, Ramanathan KB. ST segment elevation in patients with cocaine abuse and chest pain. Acute Med 2014;13:72–3. - PubMed
-
- Van de Water NS, French JK, Lund M et al. . Prevalence of factor v Leiden and prothrombin variant g20210a in patients age <50 years with no significant stenoses at angiography three to four weeks after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000;36:717–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical